|
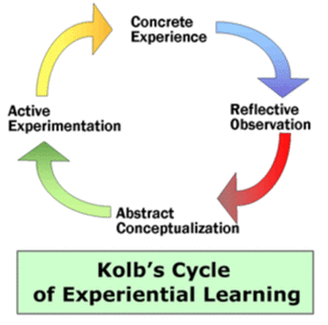
Unlocking Potential: The Key Characteristics of Experiential Learning In a rapidly changing world, traditional learning methods may not be enough to prepare individuals for the challenges they will face. This is where experiential learning comes in. This article dives deep into the key characteristics of experiential learning and how it can unlock untapped potential. Experiential learning is a hands-on approach that emphasizes learning through direct experience. It enables learners to actively engage with their environment, making connections between theory and practice. This immersive learning style promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations. If you're looking to maximize your learning potential, experiential learning is a powerful tool to consider. Unlock your potential by embracing this immersive and transformative approach to education. What is experiential learning? Experiential learning is a hands-on approach that emphasizes learning through direct experience. It goes beyond traditional classroom learning by enabling learners to actively engage with their environment, making connections between theory and practice. This immersive learning style promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations. Experiential learning involves activities such as simulations, experiments, role-playing, and field trips. These activities provide learners with the opportunity to directly interact with the subject matter, leading to a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. By actively participating in the learning process, individuals can develop practical skills that can be immediately implemented in their personal and professional lives. The importance of experiential learning Experiential learning holds immense importance in today's educational landscape. It offers a unique approach that caters to the diverse needs and learning styles of individuals. By engaging learners in hands-on activities, experiential learning helps bridge the gap between theory and practice, making education more relevant and applicable. One of the key advantages of experiential learning is its ability to build critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By actively engaging with real-world scenarios, learners are challenged to think creatively, analyze situations, and develop innovative solutions. This not only enhances their cognitive abilities but also prepares them to face the complexities of the modern world. Furthermore, experiential learning promotes self-discovery and personal growth. Through reflection and analysis of their experiences, learners gain insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This self-awareness not only enhances their learning but also contributes to their overall personal development. Characteristics of experiential learning Experiential learning is characterized by several key elements that distinguish it from traditional forms of education. These characteristics play a crucial role in unlocking the potential of learners and maximizing their learning outcomes. 1. Hands-on activities: Experiential learning involves actively engaging with the subject matter through hands-on activities. This could include experiments, simulations, field trips, or real-world projects. By directly interacting with the material, learners are able to deepen their understanding and develop practical skills. 2. Reflection: Reflection is an integral part of the experiential learning process. Learners are encouraged to reflect on their experiences, examine the outcomes, and analyze the lessons learned. This reflection process enhances self-awareness, builds personal growth, and provides valuable insights for future decision-making. 3. Active engagement: Experiential learning encourages learners to actively participate, collaborate, and experiment. By doing so, they gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and develop practical skills that can be immediately implemented. This active engagement promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts. 4. Real-world relevance: Experiential learning emphasizes the application of knowledge in real-world contexts. By engaging with authentic scenarios, learners can see the practical relevance of their learning. This not only enhances their understanding but also prepares them for real-life challenges. 5. Learner-centered: Experiential learning is learner-centered, focusing on the individual needs and interests of each learner. It recognizes that individuals have different learning styles and preferences, and therefore offers a variety of activities to cater to these diverse needs. Hands-on activities in experiential learning
Hands-on activities are at the core of experiential learning. These activities provide learners with the opportunity to actively engage with the subject matter, fostering a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Here are some examples of hands-on activities commonly used in experiential learning: 1. Simulations: Simulations recreate real-world scenarios in a controlled environment. Learners are given the opportunity to make decisions, solve problems, and experience the consequences of their actions. This allows them to gain practical experience and develop critical thinking skills. 2. Experiments: Experiments involve conducting practical tests to observe and analyze outcomes. By actively participating in experiments, learners can understand scientific concepts, develop hypotheses, and draw conclusions based on their observations. 3. Role-playing: Role-playing enables learners to step into the shoes of different characters and experience situations from different perspectives. This activity helps develop empathy, communication skills, and problem-solving abilities. 4. Field trips: Field trips provide learners with the opportunity to explore real-world environments related to their learning objectives. By visiting museums, factories, or historical sites, learners can witness firsthand how concepts are applied in real-life settings. 5. Project-based learning: Project-based learning involves learners working on real-world projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills. This activity promotes collaboration, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. Hands-on activities in experiential learning not only make the learning process more engaging but also foster practical skills that can be applied in various domains. Reflection in experiential learning Reflection is an integral part of the experiential learning process. It allows learners to analyze their experiences, make connections, and extract valuable insights. Here are some ways in which reflection enhances the learning outcomes in experiential learning: 1. Deeper understanding: Reflection enables learners to gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter. By analyzing their experiences, learners can identify patterns, make connections, and develop a more comprehensive understanding of the concepts. 2. Transfer of knowledge: Through reflection, learners can transfer their knowledge and skills to new situations. By examining the lessons learned from previous experiences, they can apply this knowledge to similar or different scenarios. 3. Personal growth: Reflection fosters personal growth by promoting self-awareness and self-improvement. By reflecting on their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, learners can develop strategies for personal development and growth. 4. Decision-making: Reflection provides valuable insights for future decision-making. By analyzing the outcomes of their experiences, learners can make informed decisions and avoid repeating past mistakes. 5. Metacognition: Reflection enhances metacognition, which is the ability to think about one's own thinking. By reflecting on their learning process, learners can gain insights into their learning preferences, strategies, and areas for improvement. Incorporating reflection into the experiential learning process is essential for maximizing the learning outcomes and enabling learners to unlock their full potential. Experiential learning in different fields - education, business, and healthcare Experiential learning is not limited to the field of education. It has also found applications in various other domains, including business and healthcare. Here's a closer look at how experiential learning is used in these fields: 1. Education: Experiential learning is widely used in the field of education to enhance the learning experience for students. It offers an alternative to traditional classroom learning by providing hands-on activities, real-world applications, and reflective practices. Experiential learning has been shown to improve student engagement, retention of knowledge, and critical thinking skills. 2. Business: Experiential learning is increasingly being recognized as a valuable tool for developing practical skills in the business world. Through internships, apprenticeships, and real-world projects, individuals can gain hands-on experience and develop the skills necessary for success in the workplace. Experiential learning also promotes teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability, which are essential skills in the business environment. 3. Healthcare: Experiential learning plays a crucial role in healthcare education. Medical students and healthcare professionals benefit from hands-on clinical experiences, simulations, and real-world case studies. This immersive learning approach helps develop clinical skills, critical thinking abilities, and the ability to make informed decisions in high-pressure situations. Experiential learning also enhances communication and collaboration skills, which are essential in the healthcare field. Experiential learning has proven to be a valuable approach in these diverse fields, offering practical and applicable learning experiences that prepare individuals for the challenges they will face. Benefits of incorporating experiential learning in the classroomIncorporating experiential learning in the classroom offers numerous benefits for both educators and students. Here are some of the key advantages of incorporating experiential learning: 1. Increased engagement: Experiential learning actively engages students in the learning process. By providing hands-on activities and real-world applications, learners become more invested in their education, resulting in increased motivation and engagement. 2. Improved retention of knowledge: Experiential learning enhances the retention of knowledge by providing learners with meaningful and memorable experiences. By actively engaging with the subject matter, learners are more likely to remember and apply what they have learned. 3. Development of practical skills: Experiential learning helps learners develop practical skills that can be immediately applied in real-world situations. By actively participating in hands-on activities, students gain the necessary experience and confidence to tackle challenges in their personal and professional lives. 4. Promotion of critical thinking: Experiential learning promotes critical thinking by challenging students to analyze, evaluate, and solve problems. Through hands-on experiences, learners develop the ability to think critically, make informed decisions, and develop innovative solutions. 5. Preparation for the real world: Experiential learning prepares students for the real world by providing them with real-world applications of their learning. By engaging with authentic scenarios, students gain practical experience and develop the skills necessary for success in their future careers. Incorporating experiential learning in the classroom not only enhances the learning experience but also prepares students for the challenges and opportunities they will encounter in their personal and professional lives. Examples of successful experiential learning programs Numerous successful experiential learning programs have been implemented worldwide, showcasing the effectiveness of this approach. Here are some examples of successful experiential learning programs: 1. Junior Achievement: Junior Achievement is a global organization that offers experiential learning programs in entrepreneurship, financial literacy, and work-readiness. Through hands-on activities, students gain practical skills and real-world experience, preparing them for success in the business world. 2. Outward Bound: Outward Bound is an outdoor education program that focuses on experiential learning in a wilderness setting. Participants engage in physically challenging activities and reflective practices, promoting personal growth, leadership skills, and teamwork. 3. Project-based learning: Project-based learning is an experiential learning approach that involves students working on real-world projects. Students collaborate, conduct research, and develop solutions to authentic problems, gaining practical skills and knowledge in the process. 4. Medical simulations: Medical simulations are a form of experiential learning used in healthcare education. Medical students and healthcare professionals engage in simulated scenarios that replicate real-world situations, allowing them to develop clinical skills, critical thinking abilities, and effective communication practices. These are just a few examples of successful experiential learning programs, highlighting the diverse applications and benefits of this transformative educational approach. Implementing experiential learning in your organization or institution If you're interested in implementing experiential learning in your organization or institution, here are some steps to get started: 1. Set clear learning objectives: Identify the desired learning outcomes and align them with the goals of your organization or institution. Clearly define what you want participants to learn and how experiential learning can help achieve those objectives. 2. Design hands-on activities: Develop hands-on activities that align with the learning objectives. These activities should provide participants with opportunities to actively engage with the subject matter, make connections, and develop practical skills. 3. Incorporate reflection: Integrate reflection practices into the experiential learning process. Provide opportunities for participants to reflect on their experiences, analyze the outcomes, and extract valuable insights. This reflection process enhances self-awareness, personal growth, and the transfer of knowledge. 4. Provide guidance and support: Ensure that participants have the necessary guidance and support throughout the experiential learning process. Facilitators or mentors can provide feedback, answer questions, and guide participants through their learning journey. 5. Evaluate and adapt: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your experiential learning program and make necessary adjustments. Gather feedback from participants, monitor the learning outcomes, and adapt the program based on the results. By following these steps, you can successfully implement experiential learning in your organization or institution, unlocking the potential of individuals and fostering a culture of continuous learning and growth. Embracing experiential learning for personal and professional growth Experiential learning is a powerful educational approach that unlocks untapped potential and prepares individuals for the challenges of the modern world. By actively engaging with hands-on activities, reflecting on experiences, and applying knowledge in real-world contexts, learners can develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and practical skills that are crucial for success. Whether in the field of education, business, or healthcare, experiential learning offers numerous benefits and applications. By incorporating experiential learning in the classroom or workplace, individuals can maximize their learning potential, enhance their personal and professional growth, and prepare themselves for a future that demands adaptability and innovation. Unlock your potential by embracing experiential learning and experience the transformative power of this immersive educational approach.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
- Home
-
Corporate
-
Team Building
>
- Team Building Activities
- Corporate Team Bonding
- Fun Team Outing
- Quotes on Teamwork
- In office Team Building Activities
- 5C Key Elements for Team Building
- Special Team Building >
- Virtual Team Building
- Top 10 Team Building Activities
- Team Building Bangalore
- Team Building Hyderabad
- Team Building Interventions
- Outbound Training >
- Leadership Programs >
- Team Outing >
- Employee Engagement >
- Behavioral Skills >
- Team Development >
- Corporate Adventure >
-
Team Building
>
- Schools
- Individuals
- Clients
- Gallery
- About us
- Articles
- Blog
- Experiential Leadership Training
- Strategic Leadership Training
- Home
-
Corporate
-
Team Building
>
- Team Building Activities
- Corporate Team Bonding
- Fun Team Outing
- Quotes on Teamwork
- In office Team Building Activities
- 5C Key Elements for Team Building
- Special Team Building >
- Virtual Team Building
- Top 10 Team Building Activities
- Team Building Bangalore
- Team Building Hyderabad
- Team Building Interventions
- Outbound Training >
- Leadership Programs >
- Team Outing >
- Employee Engagement >
- Behavioral Skills >
- Team Development >
- Corporate Adventure >
-
Team Building
>
- Schools
- Individuals
- Clients
- Gallery
- About us
- Articles
- Blog
- Experiential Leadership Training
- Strategic Leadership Training
Our Programs
OUR TRAINING DELIVERY LOCATIONS:
Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Delhi, Goa, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Vizag - India
Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Delhi, Goa, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Vizag - India

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
