Leveraging Employee EngagementSatarupa BanerjeeOutlife Outbound Training
Ravi launched his manufacturing company, StarAC India Pvt Ltd, around 7 years back. Currently, 150 employees work in this company which deals with air conditioners for homes and corporate.
The work experience of the employees ranges between 1 to 15 years. It first started by targeting individual homes and slowly penetrated the corporate market. In the initial years, the performance of the company was good. Customers were not only happy with the product quality, but also with the after sales service. The most important aspect of this company was the quality of work life. Employees were treated as assets. As a startup, it gave ample facilities to its employees to keep them happy. As a result of this, the performance of the employees was outstanding. The market share was high and employees were highly committed. This created a healthy organizational culture and scope for organizational learning for the employees. In the past 1 year, it was observed that there were too many complaints coming from the clients. The after sales service was poor and the market share of the company abruptly went down. Moreover, it was found that employee retention was becoming less and absenteeism rate increased. The employees were under performing, there was lack of motivation, high interpersonal conflict, and the entire organizational culture was going for a toss. Under this alarming situation, Ravi, along with his team of managers decided to intervene into this problem and diagnose the reasons. They hired an external OD specialist to conduct a survey to understand the reason for this deterioration of the company. The survey was conducted at StarAC and lots of issues were identified which are as follows: It was diagnosed that there was no action that could foster employee engagement in the past one year, though Ravi says that many of the employees spend time together outside the office, thus indicating that socialization facilitated at work continues outside of it too. Employees also acknowledged the same when asked about integration measures. The employees are actively encouraged to be inclusive and friendly and newcomers are given a welcoming care package as a bonus. Curiously, when asked, about employee engagement activities, few of the responding employees said that there is one, and that they are dissatisfied with it. Few other respondents said that there is no benefit program in place. Around 5 % also disclosed that they do not need any employee engagement activities. The employees confirm that there are hardly any employee engagement initiatives taken, and that career development possibilities are very limited. Though the HR manager claims that support is readily available for anyone who needs it, most of the employees disagree with the statement. According to 30% of the population, the company has a good flow of communication, though 70% claims that they barely interact with the CEO. Also, in terms of getting feedback, few claims to have received insufficient feedback while others are satisfied. Ravi and his team of managers say that they provide feedback regularly to anyone who wants it. When describing the company culture, Ravi articulates it as “family-based”, “encouraging” and “positive”. When the employees were asked to accord certain words to it, “bureaucracy”, “politics” and “role conflict” were chosen by these respondents each, with some elaboration shedding light into these choices. They also mentioned that the people who are closer to the management, gets all the favor, exercising an internal “clique” kind of power group. Along with that, overlapping tasks create a lot of friction, with employees having a feeling of job insecurity. In the past one year, the performance of the company has dropped. The cost of the company due to such turmoil within and amongst employees has been exorbitantly high. The human resources of the company are getting drained undermining goals of the company. Employee disengagement vests on three pillars ,which HRs should focus on. These are self, team and organization culture. Let us now see the challenges Ravi’s organization was facing at these three levels. Self Employees were in blind spots. They became a poor fit because of their personality conflicts and difficulty in adapting with the here and now. They had lack of engagement activities which resulted into ambiguous understanding of roles and expectations. Employees lacked requisite skills to deal with organizational politics and power struggle. Team Disengaged employees lacked interactive communication skills. They listened and communicated inarticulately, fostering less open interpersonal communication. The overall team performance got distorted due to interpersonal conflict, power struggle, etc. These lead to complexity, de-motivation and stress amongst the team members. As a team, employees failed to understand mode of transactions (ego states) amongst team members. Organizational Culture Lack of understanding of self, organizational politics and inability to engage with team members gave rise to a culture where employees were less committed, and the outcomes were neither well defined nor well understood. The operational element, the manager, was lacking in this culture, who coaches individual performance to align with strategy and purpose to reach those well defined outcomes. Ravi in collaboration with his team of managers and the external OD specialist created an action plan so as to bring about a change in the behavior of the employees. They were focusing on specific outcomes such as increasing the sales and post sales service, employee retention and well being, harmonious organizational culture and improved quality of work life through employee engagement programs. They incorporated employee exchange sessions thrice a week where employees will be required to do some activities on team building, interpersonal skills, communication so as to better gel with other team members to understand self and others. The company also asked the HR managers to personally counsel the employees to have a better understanding of their needs. Reinforcement measures like introducing complimentary notes to star performers across the company through emails and whatsapp groups were taken to motivate employees to have a sense of belongingness. An Employee Wellness Record Software was created whereby the employees could feed in their areas of dissatisfaction which will be addressed by the HR team. Difficult employees were separately counseled by the HR manager. Ravi also took part in informal meetings once in a month to get feedback from the employees on their working conditions. Employee rewards and recognition was modified and upgraded. As a result of all these, there was a gradual positive change in employee behavior and performance in the first six months. Inter departmental employee involvement programs geared up the morale of the employees whereby the sales increased and people reported that they feel happy and energized than before. At the end of one year of incorporating these intervention strategies, there was a change in the behavior, performance and productivity demonstrated by the employees. People were happy because Ravi also modified his mode of communication where he was more approachable and empathetic to employee needs. The company started functioning much better than before. From the above scenario, we can infer that Ravi’s company is not the only one dealing with employee engagement issues. Rather, most of the corporate is facing this issue of disengaged employees, resulting in low ROI. The biggest challenge corporate are trying to cope with is to demonstrate significantly higher levels of performance and productivity between engaged and disengaged employees. Engagement goes further than ‘commitment’ and ‘motivation’ in the management literature (Woodruffe, 2006 as cited in CIPD, 2006a). As per a report by Deloitte, 87% of the executives rated culture and employee engagement as the biggest HR challenge. Gallup engagement survey shows that employee communication strategy is a pre requisite for a better performance which in turn is required for a positive outcome. In order to achieve organizational goals, let us now see the various strategies used by corporate to increase trust, integrity and involvement within the employees through employee engagement programs. Enhancing employee engagement through training and development
In order to cope with this talent disengagement, HR needs to create and hone their culture of engagement. Several models of employee engagement are used to deal with challenging scenarios at workplace, out of which, the Blessing White Employee Engagement Model suffices the purpose of achieving the sustainable employee engagement required for an organization to reach its goals.
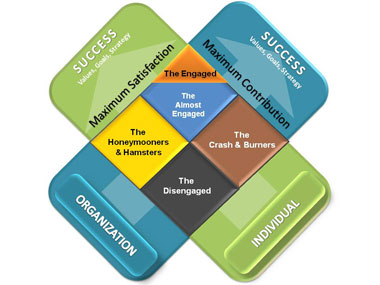
Full engagement depicts an alignment of maximum job satisfaction (“I like my job and do it well”) with maximum job contribution (“I assist my organization to achieve its goals”). The employee’s engagement level contains items that reflect the two axes of contribution and satisfaction. By plotting a given population against the two axes, 5 distinct employee segments are identified. This is represented as
The Engaged: The personal and organizational interests of the employees align. The employees are satisfied and add success to the company. These employees can transit over time to any of the three adjacent segments, which may impact workforce morale and motivation.
Almost Engaged: These employees are high performers and satisfied with their jobs. They are aware of their job functions. They are highly employable .They take minimal time to achieve the maximum goal. The Honeymooners &Hamsters: Honeymooners are novice to the organization. They are yet to clearly understand how they can best contribute. Managers should move them out of this temporary holding area to full alignment and productivity. Hamsters may be working hard, but are in effect “spinning their wheels,” working on unimportant tasks, contributing little to the success of the organization. If organizations don’t deal with them, other employees may grow resentful or have to pick up the slack. The Crash & Burners: These employees are disillusioned and potentially exhausted. They are neither successful nor satisfied. They may leave, or they are more likely to become disengaged. When they do, they often bring down those around them. The Disengaged: These employees are the most disconnected from organizational priorities. They often feel underutilized and are clearly not getting what they need from work. They are skeptical and likely to induce negativity within the team. If they cannot be coached properly, then exit interviews are their last resort.
RECOMMENDED EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT TOOLS TO IMPROVE ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE
Various intervention strategies are drivers of employee engagement where they feel a sense of belongingness and valued within the organization. Various models suggest us elements to uplift employee morale and motivation so as to keep them engaged and committed to the organization. The Zinger Model of Employee Engagement (2009) is one such tool which demonstrates intervention strategies at three levels, viz. the organization contribution, the leadership inputs and individual employee contribution to employee engagement. Broadly the strategic interventions would include some of the following changes:
Employee Experience (EX) is the latest evolution from employee engagement. Mckinsey defines EX as “companies and their people working together to create personalized, authentic experiences that ignite passion and tap into purpose to strengthen individual, team, and company performance.” It is a more human centric approach in directing employees towards organizational performance. Employee engagement is unidirectional- company to employee, based on the surveys of employee insights. However, it does not reflect the true sense of how work gets done. Millennials comprise 30% of the organizational population which will leverage to 75% by 2025. The Mckinsey report enlists certain critical factors to improve employee experience which are as follows:
Employee engagement in workplace pave creative ways to communicate with trainees in forms of inbound and outbound trainings, competency mapping, need analysis, performance coaching, engagement through high performing employees, thus creating motivation and reducing stress.
HR managers along with the LnD department should focus more on career development tools, set expected individual and team behaviors and reinforce key competencies. A network of engaged workforce can help an organization make necessary changes to create a dynamic work environment and thriving teams. Outlife is a specialist experiential learning and outbound training provider that conducts behavioral skills training, team building and management development programs using experiential education methodology. The OBT training and team building programs are hands on, engaging, fun, exciting and use adult learning methodology. Outlife conducts employee engagement programs based on three broad categories such as recreational, educational and developmental. Recreational - Focus is on the team experiencing fun and feel good factor. Educational - Focus is on the team learning specific learning objectives to bring a change in the way they behave, think or perceive. Mostly employed for team building sessions, behavioral skills training, outbound training. Developmental - Focus is on learning and knowledge to bring a change in habits, motives, behaviors and attitude. Mostly Employed in Outdoor Management Development and Leadership Development Programs. While there are many ideas and activities around employee engagement, Outlife can help create motivation and belongingness in your organization through the following employee engagement ideas and activities. These include
Webliography
2 Comments
|
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
- Home
-
Corporate
-
Team Building
>
- Team Building Activities
- Corporate Team Bonding
- Fun Team Outing
- Quotes on Teamwork
- In office Team Building Activities
- 5C Key Elements for Team Building
- Special Team Building >
- Virtual Team Building
- Top 10 Team Building Activities
- Team Building Bangalore
- Team Building Hyderabad
- Team Building Interventions
- Outbound Training >
- Leadership Programs >
- Team Outing >
- Employee Engagement >
- Behavioral Skills >
- Team Development >
- Corporate Adventure >
-
Team Building
>
- Schools
- Individuals
- Clients
- Gallery
- About us
- Articles
- Blog
- Experiential Leadership Training
- Strategic Leadership Training
- Home
-
Corporate
-
Team Building
>
- Team Building Activities
- Corporate Team Bonding
- Fun Team Outing
- Quotes on Teamwork
- In office Team Building Activities
- 5C Key Elements for Team Building
- Special Team Building >
- Virtual Team Building
- Top 10 Team Building Activities
- Team Building Bangalore
- Team Building Hyderabad
- Team Building Interventions
- Outbound Training >
- Leadership Programs >
- Team Outing >
- Employee Engagement >
- Behavioral Skills >
- Team Development >
- Corporate Adventure >
-
Team Building
>
- Schools
- Individuals
- Clients
- Gallery
- About us
- Articles
- Blog
- Experiential Leadership Training
- Strategic Leadership Training
Our Programs
OUR TRAINING DELIVERY LOCATIONS:
Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Delhi, Goa, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Vizag - India
Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Delhi, Goa, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Vizag - India

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
