Online Game Based Experiential Learning
Game Based Experiential Learning - GBEL takes advantage of experiential learning theory, gaming technologies and digital connectivity to create a fun, motivating, and interactive virtual learning environment that promotes education and learning.
Experiential learning theory has long inspired educators and game designers to incorporate Experiential Learning as a important component of digital game based learning to create an immersive learning environment.
Games have been part of human cultures since ages and people have been playing games for both entertainment and learning for centuries. Chess is one the oldest games that is still played commonly. Video games and computers games have become popular since the 1980'sand have been primarily used for entertainment purposes.
Over the last 3 decade games have increasingly being used for learning simulations, education and training both in the academia, government and businesses. Experiential Game Based learning is however focused more on education, learning and training while keeping the element of fun, entertainment and engagement alive and immersive.
Experiential learning theory has long inspired educators and game designers to incorporate Experiential Learning as a important component of digital game based learning to create an immersive learning environment.
Games have been part of human cultures since ages and people have been playing games for both entertainment and learning for centuries. Chess is one the oldest games that is still played commonly. Video games and computers games have become popular since the 1980'sand have been primarily used for entertainment purposes.
Over the last 3 decade games have increasingly being used for learning simulations, education and training both in the academia, government and businesses. Experiential Game Based learning is however focused more on education, learning and training while keeping the element of fun, entertainment and engagement alive and immersive.
What is Game Based Learning
Game-based learning uses online video games that are designed for education and development contexts to reach specific learning objectives for Corporate Training or School Education.
In a game-based learning environment, users learn new concepts and practice skills in a risk-free and safe environment. Their progress in the game is directly related to their understanding of the knowledge and skills being taught through the game dynamics.
The goal of game-based learning is engagement, education and behavioral change. Game based learning promotes excitement, stimulation, engagement and the feeling of accomplishment and is a great means to facilitate learning and combine meaningful learning along with fun.
In a game-based learning environment, users learn new concepts and practice skills in a risk-free and safe environment. Their progress in the game is directly related to their understanding of the knowledge and skills being taught through the game dynamics.
The goal of game-based learning is engagement, education and behavioral change. Game based learning promotes excitement, stimulation, engagement and the feeling of accomplishment and is a great means to facilitate learning and combine meaningful learning along with fun.
Types and Uses of Game Based Learning
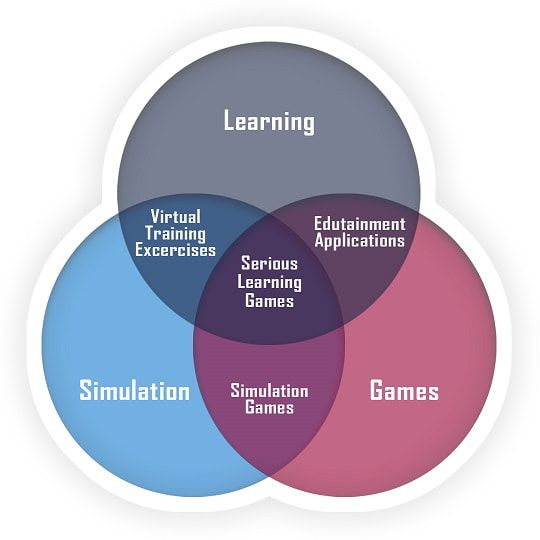
Game Based Learning include variety of uses and applications depending on the method and desired outcomes. They are primarily three broad areas that game based learning incorporates: Games, Simulation and Learning. Depending on the combination of these elements the type of game and outcome differs.
Some of the different type of game based learning are:
Some of the different type of game based learning are:
Simulation games – Simulations are games that simulates something happening in real life. Simulation games are used for the acquisition or training of different skills, teaching effective behavior in the context of simulated conditions or situations. Simulation games gives the learners opportunity to solve problems and participate in situations, impossible or inappropriate in real life.
The simulated environment allows participants to experience something that is too expensive, too risky or even physically impossible to achieve in the real world. Example of simulations would be learning to fly a plane. learning to operate medical procedures, learning to negotiate or be assertive through role plays.
Edutainment Games – Edutainment games focus on learning outcomes and presenting content as part of the game experience. They are designed both for education and enjoyment purposes.
Virtual Training Exercises are instructor led training virtual simulated exercises delivered remotely over a video conference like zoom that focus on engaging learners for fun or learning. Virtual training can be used for employee engagement or team building.
Serious Games are games that use a combination of games, simulation and learning and are aimed at achieving education, training and information goals. Serious games are classified as serious as they are designed only for education and learning purposes.
Serious games are used for non-entertaining purpose (serious) with a video game structure (gameplay). Serious games are available in Single Player format that are mostly used for on-boarding or value/culture education. Multi-player serious games include other players as either competitors or teammates that help with experiencing and learning behaviors on team building, Collaboration, Leadership skills training, Managerial Effectiveness training etc.
Serious gaming can be a one time session focused on a key learning outcome or a journey of continuous sessions where the players go through multiple gaming sessions along with building skills in various aspects.
In serious games there is aspect of transfer of learning from the game to real life and from real life to the game which is achieved through processing experiences in the game and in real life and how it effects each other in a journey of playing multiple sessions. This is achieved with a facilitator and through regular reflection and feedback sessions with the team.
The simulated environment allows participants to experience something that is too expensive, too risky or even physically impossible to achieve in the real world. Example of simulations would be learning to fly a plane. learning to operate medical procedures, learning to negotiate or be assertive through role plays.
Edutainment Games – Edutainment games focus on learning outcomes and presenting content as part of the game experience. They are designed both for education and enjoyment purposes.
Virtual Training Exercises are instructor led training virtual simulated exercises delivered remotely over a video conference like zoom that focus on engaging learners for fun or learning. Virtual training can be used for employee engagement or team building.
Serious Games are games that use a combination of games, simulation and learning and are aimed at achieving education, training and information goals. Serious games are classified as serious as they are designed only for education and learning purposes.
Serious games are used for non-entertaining purpose (serious) with a video game structure (gameplay). Serious games are available in Single Player format that are mostly used for on-boarding or value/culture education. Multi-player serious games include other players as either competitors or teammates that help with experiencing and learning behaviors on team building, Collaboration, Leadership skills training, Managerial Effectiveness training etc.
Serious gaming can be a one time session focused on a key learning outcome or a journey of continuous sessions where the players go through multiple gaming sessions along with building skills in various aspects.
In serious games there is aspect of transfer of learning from the game to real life and from real life to the game which is achieved through processing experiences in the game and in real life and how it effects each other in a journey of playing multiple sessions. This is achieved with a facilitator and through regular reflection and feedback sessions with the team.
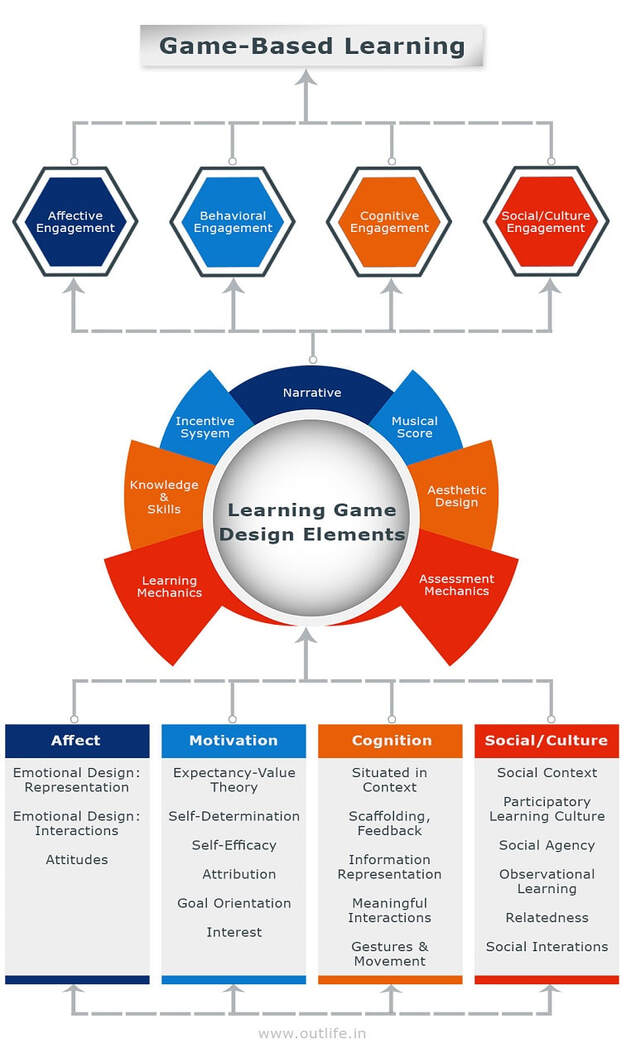
Elements of Serious Game Based Learning
Its takes serious efforts to create serious games that can simulate real world environments. it requires a lot of talent, a lot of time and a lot of money. Creating a game requires the work of skilled writers, game designers, artists, game architects, database developers, user interface specialists along with subject matter experts as for fact verification, instructional design and testing.
Most game-based learning systems tend to have the following elements that ensure they work properly and are effective for education and training purposes.
1. An Engaging Story. Most games have a plot or a main story that is front loaded. It may be a invitation to rescue or save the planet against a disaster or to achieve certain tasks along with learning all the necessary skills that are similar to the learning objectives like motivating and rewarding their colleagues, resolving conflicts, delegating tasks or coaching them. Stories, Plots and challenges motivate the players and engage them emotionally into the game environment.
2. Game Dynamics and Design: Game dynamics and design, include the rankings, status, rewards, badges or points systems all which are based on gamification and tend to animate and motivate the players all along the game: the Design structure and mechanics of the game should have an appropriate relationship to the content.
3. Real Consequences and personal feedback : games offer immediate and personalized feedback. Each player interacts directly with the game and instantly receives a reward or a punishment. The consequences are real and the participants can know where they have gone wrong and can try to do better next time which serves as a a powerful learning and skill building tool.
4. Game Simulation. The game reproduces or imitates a real life situation or event. Using fictitious characters and by recreating scenarios, players find themselves immersed in a virtual environment that is similar to their real world. These simulations make it possible for participants to interact with a new reality and to practice the skills and concepts they have acquired during the game and transfer the learning's to their real life. Simulations are also designed to reduce program cost, schedule for mission critical environments like the doctors, army, pilots and law enforcement.
5. Game Aesthetics: Aesthetics refers to the sensory phenomena that the player engages with in the game in form of Visual, aural, haptic, embodied feedback experienced as pleasure, joy, emotion, sociability, formgiving in reference to the aesthetic experience of the game. Aesthetics is make-believe experience where attention is firmly fixed upon the immersive and emotional components of the visual, aural, haptic feedback and excludes the awareness of other surrounding objects or events.
6. Motivation and Engagement: Motivation along with game mechanics, simulation, consequences, feedback, and storytelling drives widespread engagement and buzz. This is also because the successful adaptation of desired behaviors create retention and application of competencies. Intrinsic motivations include peer recognition and personal satisfaction and extrinsic motivations include career advancement and position based on skill development and performance.
7. Learning Goals. The key differentiation of game based learning is that their purpose is to teach specific learning objectives. Games for Learning have a purpose that is not just entertainment but a certain educational or training aspect.
Most game-based learning systems tend to have the following elements that ensure they work properly and are effective for education and training purposes.
1. An Engaging Story. Most games have a plot or a main story that is front loaded. It may be a invitation to rescue or save the planet against a disaster or to achieve certain tasks along with learning all the necessary skills that are similar to the learning objectives like motivating and rewarding their colleagues, resolving conflicts, delegating tasks or coaching them. Stories, Plots and challenges motivate the players and engage them emotionally into the game environment.
2. Game Dynamics and Design: Game dynamics and design, include the rankings, status, rewards, badges or points systems all which are based on gamification and tend to animate and motivate the players all along the game: the Design structure and mechanics of the game should have an appropriate relationship to the content.
3. Real Consequences and personal feedback : games offer immediate and personalized feedback. Each player interacts directly with the game and instantly receives a reward or a punishment. The consequences are real and the participants can know where they have gone wrong and can try to do better next time which serves as a a powerful learning and skill building tool.
4. Game Simulation. The game reproduces or imitates a real life situation or event. Using fictitious characters and by recreating scenarios, players find themselves immersed in a virtual environment that is similar to their real world. These simulations make it possible for participants to interact with a new reality and to practice the skills and concepts they have acquired during the game and transfer the learning's to their real life. Simulations are also designed to reduce program cost, schedule for mission critical environments like the doctors, army, pilots and law enforcement.
5. Game Aesthetics: Aesthetics refers to the sensory phenomena that the player engages with in the game in form of Visual, aural, haptic, embodied feedback experienced as pleasure, joy, emotion, sociability, formgiving in reference to the aesthetic experience of the game. Aesthetics is make-believe experience where attention is firmly fixed upon the immersive and emotional components of the visual, aural, haptic feedback and excludes the awareness of other surrounding objects or events.
6. Motivation and Engagement: Motivation along with game mechanics, simulation, consequences, feedback, and storytelling drives widespread engagement and buzz. This is also because the successful adaptation of desired behaviors create retention and application of competencies. Intrinsic motivations include peer recognition and personal satisfaction and extrinsic motivations include career advancement and position based on skill development and performance.
7. Learning Goals. The key differentiation of game based learning is that their purpose is to teach specific learning objectives. Games for Learning have a purpose that is not just entertainment but a certain educational or training aspect.
Gameplay, Mechanics and Dynamics of Game Based Learning
What is Gamification
Gamification is the integration of game elements like point systems, leaderboards, badges, or other elements related to games into learning activities in order to increase engagement and motivation.
What is Gameplay.
Gameplay is how the players interacts with the game in terms of rules, plot, objectives, challenges. Gameplay is the pattern defined through the game rules which creates a engaging and emotional connection between the player and the game through the many challenges, plots and rewards.
What are Game Mechanics?.
Game Mechanics are the basic actions, processes, visuals, and control mechanisms that are used to “gamify” a game. Game mechanics are the building blocks of gamification of the game with the rules and rewards that make up gameplay and create an engaging and immersive experience.
What Are Game Dynamics?
Game Dynamics refers to a set of emotions, behavior and desires that gamification leverages to relate with people. Game dynamics are built upon Game Mechanics to motivate and engage participants throughout the game.
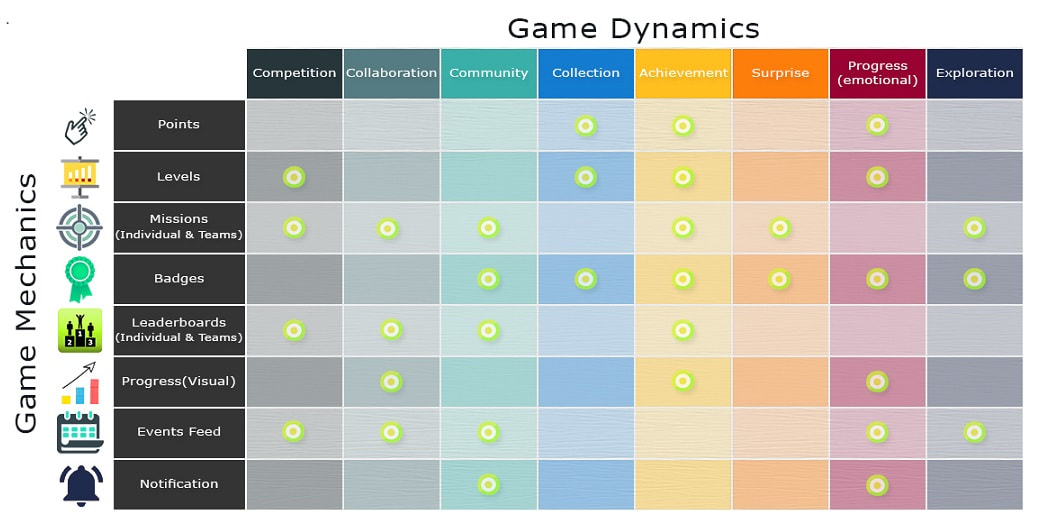
Game Dynamics include:
Gamification is the integration of game elements like point systems, leaderboards, badges, or other elements related to games into learning activities in order to increase engagement and motivation.
What is Gameplay.
Gameplay is how the players interacts with the game in terms of rules, plot, objectives, challenges. Gameplay is the pattern defined through the game rules which creates a engaging and emotional connection between the player and the game through the many challenges, plots and rewards.
What are Game Mechanics?.
Game Mechanics are the basic actions, processes, visuals, and control mechanisms that are used to “gamify” a game. Game mechanics are the building blocks of gamification of the game with the rules and rewards that make up gameplay and create an engaging and immersive experience.
What Are Game Dynamics?
Game Dynamics refers to a set of emotions, behavior and desires that gamification leverages to relate with people. Game dynamics are built upon Game Mechanics to motivate and engage participants throughout the game.
Game Dynamics include:
- Competition
- Collaboration
- Community
- Collection
- Achievement
- Surprise
- Progress (visual and emotional)
- Exploration
Game Dynamics include human desires and motivation. They trigger extrinsic and intrinsic motivation by not only defining but propelling the Game Dynamics further. The following are some Game Dynamics built into gameplay.
Points: Points are used to indicate status, identify high priority activities or used to trade in real or virtual goods. Game Dynamics related to Points include Achievement and Progress. Users want to feel rewarded and Points can help users keep score.
Levels: Levels show how users reach a milestone, program status, or areas of accomplishment. This can also show long-term or sustained achievement within the gamification program. Levels within game mechanics taps into the human desires and motivations (Game Dynamics) of Competition, Collection, Achievement, and Progress.
Missions: Missions provide objectives for users to accomplish as a team or as an individual. Once the mission is completed (or challenge overcome), users may feel a sense of accomplishment. Game Dynamics that always work with Missions include Competition, Community, Achievement, Surprise, and Exploration.
Badges: Badges are wont to demonstrate mastery over important tasks and goals. . These visual indicators of accomplishment can also communicate skill or expertise within a group. Game Dynamics related to Badges include: Community, Collection, Achievement, Surprise, Exploration.
Leaderboards: Leaderboards show how users/teams are progressing against each other. A team/individual leading in the game can inspire the other team/individual to attempt to perform better. A leaderboard could trigger competition among another team/individual to outperform the current leader. Key Game Dynamics related to Leaderboards include Competition, Collaboration, Community, Achievement.
Progress : A visualization of Progress shows users where they are in completing missions, challenges and in the overall game user journey. Game Dynamics associated with progress are Achievement, Progress (emotional).
Events Feed: Events Feed enables users to see how everybody else in the game is doing; participants get to know about themselves and their colleagues who have achieved or completed a mission and progressed to the next level. Events Feed can be used to motivate other users to do certain actions so their progress could be broadcasted on the Events Feed to others. Game Dynamics associated with events are Exploration, Competition, Collaboration, Community, and Progress
How Game Mechanics Impact Motivation: The essence of gamification is the application of game mechanics to “gamify” an activity. Game mechanics are the rules and rewards that build the foundation of gameplay.
Game mechanics, when strategically and tactically deployed in accord with Game Dynamics, can make the gamification challenging, fun, rewarding and intrinsically inspire emotions and bring out the desired learning outcomes. The content, skills and learning outcomes are built into the game through use of game mechanics.
Points: Points are used to indicate status, identify high priority activities or used to trade in real or virtual goods. Game Dynamics related to Points include Achievement and Progress. Users want to feel rewarded and Points can help users keep score.
Levels: Levels show how users reach a milestone, program status, or areas of accomplishment. This can also show long-term or sustained achievement within the gamification program. Levels within game mechanics taps into the human desires and motivations (Game Dynamics) of Competition, Collection, Achievement, and Progress.
Missions: Missions provide objectives for users to accomplish as a team or as an individual. Once the mission is completed (or challenge overcome), users may feel a sense of accomplishment. Game Dynamics that always work with Missions include Competition, Community, Achievement, Surprise, and Exploration.
Badges: Badges are wont to demonstrate mastery over important tasks and goals. . These visual indicators of accomplishment can also communicate skill or expertise within a group. Game Dynamics related to Badges include: Community, Collection, Achievement, Surprise, Exploration.
Leaderboards: Leaderboards show how users/teams are progressing against each other. A team/individual leading in the game can inspire the other team/individual to attempt to perform better. A leaderboard could trigger competition among another team/individual to outperform the current leader. Key Game Dynamics related to Leaderboards include Competition, Collaboration, Community, Achievement.
Progress : A visualization of Progress shows users where they are in completing missions, challenges and in the overall game user journey. Game Dynamics associated with progress are Achievement, Progress (emotional).
Events Feed: Events Feed enables users to see how everybody else in the game is doing; participants get to know about themselves and their colleagues who have achieved or completed a mission and progressed to the next level. Events Feed can be used to motivate other users to do certain actions so their progress could be broadcasted on the Events Feed to others. Game Dynamics associated with events are Exploration, Competition, Collaboration, Community, and Progress
How Game Mechanics Impact Motivation: The essence of gamification is the application of game mechanics to “gamify” an activity. Game mechanics are the rules and rewards that build the foundation of gameplay.
Game mechanics, when strategically and tactically deployed in accord with Game Dynamics, can make the gamification challenging, fun, rewarding and intrinsically inspire emotions and bring out the desired learning outcomes. The content, skills and learning outcomes are built into the game through use of game mechanics.
Benefits of Serious Game Based Learning |
|
|
Game based learning promotes excitement, stimulation, engagement and the feeling of accomplishment and are a great means to facilitate learning and combine meaningful learning with fun.
Games can be professionally facilitated, to provide teams with an immersive, challenging, and fun environment to learn behavioral, team and leadership skills in a fun and engaging online learning environment. Games promote enhancing
|
|
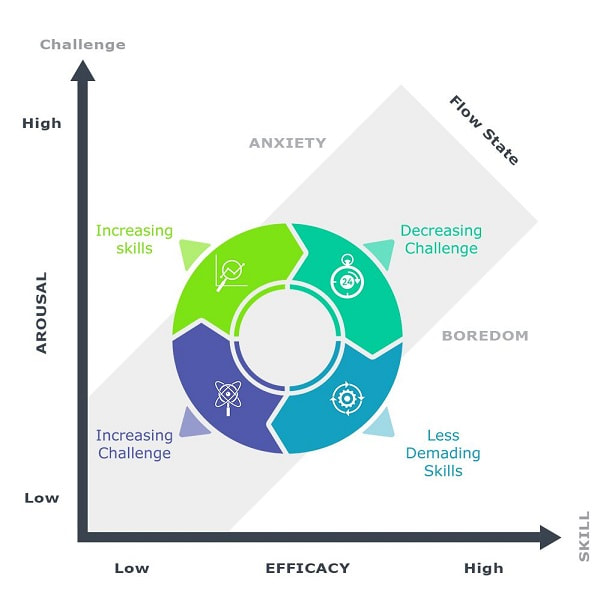
Flow Experience in Gameplay
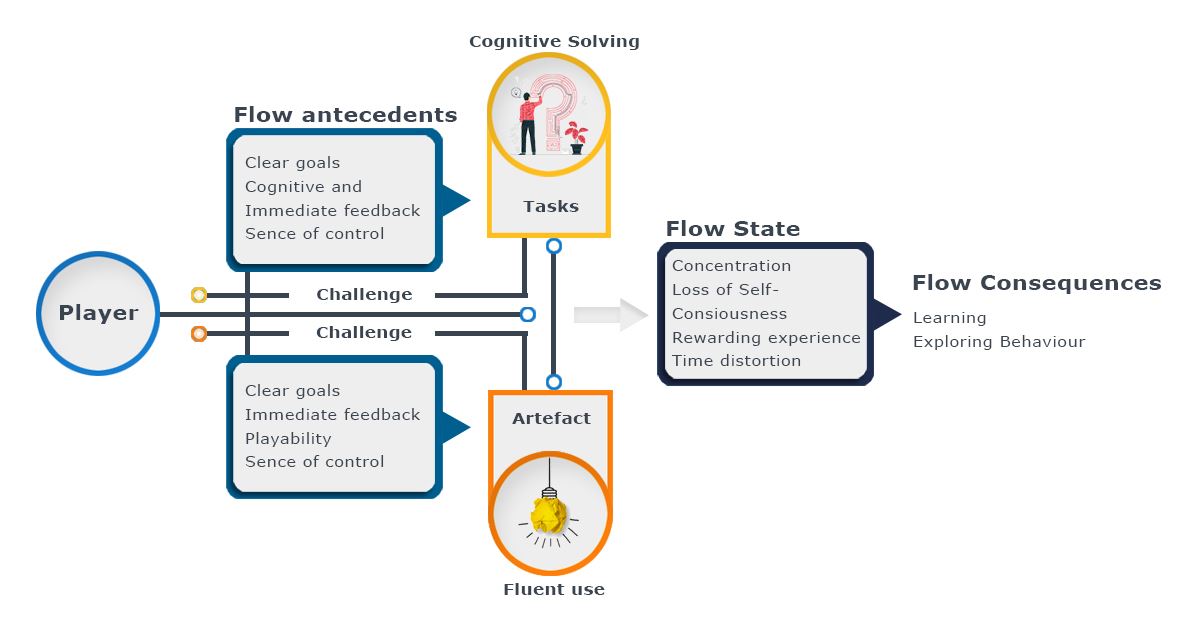
Games are designed to generate a positive affect in players and are most successful and engaging when they facilitate the flow experience. Csikszentmihalyi describes Flow as a state of complete absorption or engagement in an activity and refers to the optimal experience
Gameplay creates an optimal experience for the players where they get into a emotional and psychological state and get so involved with the game activity that nothing else seems to matter to them.
Gameplay creates an optimal experience for the players where they get into a emotional and psychological state and get so involved with the game activity that nothing else seems to matter to them.
The state of flow generated by gameplay experience are focused attention on the goal, engagement with game feedback, potential control over game dynamics, playfulness with speed and ease of use .
The flow experience itself comprises a merging of action and awareness, concentration, a sense of control over activity , time distortion, and telepresence. The flow experience leads to positive impact such as increased learning and increased exploratory and risk taking behavior.
The gameplay continues to immersive the player by using the zone of proximal development into the gameplay where a player in a flow state faces increasing challenges in the game as per his skills and he progressing in the game the game becomes more difficult to keep the player in the flow experience.
The flow experience itself comprises a merging of action and awareness, concentration, a sense of control over activity , time distortion, and telepresence. The flow experience leads to positive impact such as increased learning and increased exploratory and risk taking behavior.
The gameplay continues to immersive the player by using the zone of proximal development into the gameplay where a player in a flow state faces increasing challenges in the game as per his skills and he progressing in the game the game becomes more difficult to keep the player in the flow experience.
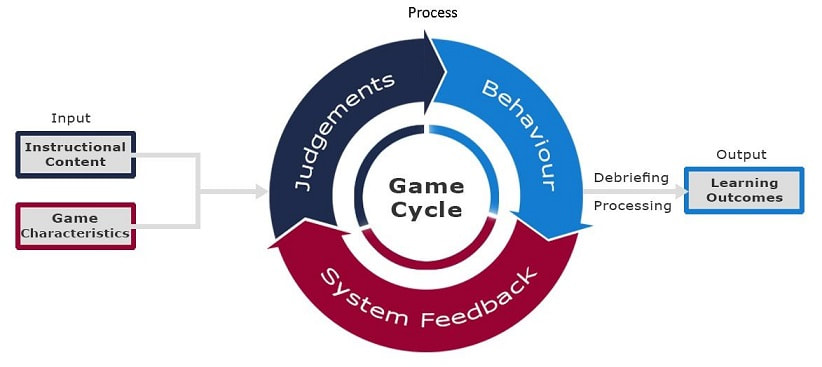
Facilitation and Processing of Serious GamePlay
The game based learning platform includes game dynamics that represent real life situations and has immediate consequences and rewards that motivate continuous emotional engagement.
Though the game includes the desired learning outcomes as part of the game journey where education content and concepts are built in, in most cases the game experience in itself is not enough for learning transference and requires a skilled facilitator to process the experience and connect with real life.
The facilitation of the gaming based learning experience is done by experienced facilitators who create a safe environment for the participants to practice and receive feedback from the gaming experience, facilitator and other players for improvement.
Though the game includes the desired learning outcomes as part of the game journey where education content and concepts are built in, in most cases the game experience in itself is not enough for learning transference and requires a skilled facilitator to process the experience and connect with real life.
The facilitation of the gaming based learning experience is done by experienced facilitators who create a safe environment for the participants to practice and receive feedback from the gaming experience, facilitator and other players for improvement.
The facilitation includes debriefing the gaming experience and holding facilitated discussions around the individual and team actions. Learning models are introduced wherever necessary and the gaming experience generalized with real-life performance, where participants are invited to change behavior or take actions that promote, individual and team growth and development.
Participants are able to instantly see their behaviors and areas of improvement developing insights, awareness and learning that can be applied in their real life interactions. Games are effective ways to address the cognitive, emotional and social aspect of the learner and bring change in their realworld.
Participants are able to instantly see their behaviors and areas of improvement developing insights, awareness and learning that can be applied in their real life interactions. Games are effective ways to address the cognitive, emotional and social aspect of the learner and bring change in their realworld.
Experiential Learning in Serious Gameplay
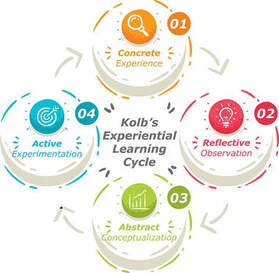
The Facilitation of the Game Experience is based on the experiential learning cycle which includes the following four phases;
1. Concrete experience (Feeling) - Experiencing the Gameplay
2. Reflective Observation (Observing) - Observing, recalling and reflecting on emotions and behaviors during gameplay.
3. Abstract conceptualization(Thinking) - Understanding and Interpreting causes, decisions and actions taken during gameplay and generalising it with personal or group behaviors.
4. Active experimentation (Doing). - Experimenting and applying insights and new behaviors in gameplay and real life.
1. Concrete experience (Feeling) - Experiencing the Gameplay
2. Reflective Observation (Observing) - Observing, recalling and reflecting on emotions and behaviors during gameplay.
3. Abstract conceptualization(Thinking) - Understanding and Interpreting causes, decisions and actions taken during gameplay and generalising it with personal or group behaviors.
4. Active experimentation (Doing). - Experimenting and applying insights and new behaviors in gameplay and real life.
Uses of Game Based Learning
Game Based Learning and Serious Games focus on education and developmental goals like acquiring soft skills, behavioral and leadership skills by engaging the participants in variety of individual and group tasks designed to develop group members competencies and enhance their ability to work together effectively.
The following are some of the many behavior competencies that can be learnt from participating in the Game Based Learning.
The following are some of the many behavior competencies that can be learnt from participating in the Game Based Learning.
|
|
Game Based Learning Examples
Online - Game Based Learning Offerings
Our Game Based Learning Offering include the following:
1. Multiplayer Serious Game Designed to meet your desired learning outcomes.
2. Multiplayer Game Based Platform for Leadership Skills, Team Building, Collaboration and Behavioral Skills
3. Gaming experiences for Employee Engagement and Onboarding based on your company values and procedures.
1. Multiplayer Serious Game Designed to meet your desired learning outcomes.
2. Multiplayer Game Based Platform for Leadership Skills, Team Building, Collaboration and Behavioral Skills
3. Gaming experiences for Employee Engagement and Onboarding based on your company values and procedures.
Our Offerings include understanding your learning needs, design gameplay to suite your learning outcomes and facilitate gaming experiences that range from 2 Hour to 4 Hours, Multiple Day Learning Journeys