What is Experiential Learning
Experiential learning methodology is a well-known model in education, training, facilitation, coaching and organizational development.
Experiential learning is an immersive, participant focused, active approach to learning that involves experiential learners of all ages, backgrounds and experience levels in a emotionally engaging learning experience
Experiential Learning is a subset of the broader field of Experiential Education which is a teaching philosophy with a multidisciplinary approach toward learning.
Experiential learning focuses on creating experiences that have a practical application of knowledge and skills to real-world experiences to increase learner's knowledge and develop competence in skills and behaviors.
It is effectively used in schools, higher education, therapy, corporate training and other areas for educational learning, personal development and skills building.
According to the Association for Experiential Education, experiential learning can be summed up in the phrase “challenge and experience followed by reflection and application leading to learning and growth.”
Experiential learning is not new and is an age old concept. Aristotle spoke of it around 350 BC when he wrote in the Nicomachean Ethics "For the things we have to learn before we can do them, we learn by doing them." Confucius also spoke about it at around the same period. However, as an articulated educational approach, experiential learning is very recent.
The concept of experiential learning was first explored in education and learning context by John Dewey, Kurt Hahn, Kurt Lewin and Jean Piaget, among others. It was made popular by David A. Kolb.
Experiential Learning can be defined as one that:
Experiential learning is an immersive, participant focused, active approach to learning that involves experiential learners of all ages, backgrounds and experience levels in a emotionally engaging learning experience
Experiential Learning is a subset of the broader field of Experiential Education which is a teaching philosophy with a multidisciplinary approach toward learning.
Experiential learning focuses on creating experiences that have a practical application of knowledge and skills to real-world experiences to increase learner's knowledge and develop competence in skills and behaviors.
It is effectively used in schools, higher education, therapy, corporate training and other areas for educational learning, personal development and skills building.
According to the Association for Experiential Education, experiential learning can be summed up in the phrase “challenge and experience followed by reflection and application leading to learning and growth.”
Experiential learning is not new and is an age old concept. Aristotle spoke of it around 350 BC when he wrote in the Nicomachean Ethics "For the things we have to learn before we can do them, we learn by doing them." Confucius also spoke about it at around the same period. However, as an articulated educational approach, experiential learning is very recent.
The concept of experiential learning was first explored in education and learning context by John Dewey, Kurt Hahn, Kurt Lewin and Jean Piaget, among others. It was made popular by David A. Kolb.
Experiential Learning can be defined as one that:
- Combines direct experience with focused reflection.
- Builds on past knowledge and experiences.
- Requires active involvement in meaning construction.
- Encourages collaboration and exchange of ideas and perspectives.
- Can be course focused or in-class, community focused, or work focused.
Experiential Learning Theory
Experiential learning theory (ELT) is a framework developed by David Kolb that explains how people learn through direct experience, reflection, and experimentation. Kolb's theory proposes that learning involves four distinct modes of processing which include 4 stages and 4 learning styles.
According to ELT, learning occurs through a cyclical process that involves experiencing, reflecting, conceptualizing, and experimenting. Kolb also emphasizes that people tend to have a preferred learning style, but effective learning involves using all four modes of processing.
ELT has been widely applied in various contexts, including education, business, and psychology, and has been used to design experiential learning activities and programs that promote deep learning and personal and professional growth.
According to ELT, learning occurs through a cyclical process that involves experiencing, reflecting, conceptualizing, and experimenting. Kolb also emphasizes that people tend to have a preferred learning style, but effective learning involves using all four modes of processing.
ELT has been widely applied in various contexts, including education, business, and psychology, and has been used to design experiential learning activities and programs that promote deep learning and personal and professional growth.
How Experiential Learning Works
The basic model of experiential learning cycle is "Do Reflect Decide".
Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory (David Kolb, 1984) defines experiential learning as "the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping and transforming experience."
Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory (David Kolb, 1984) defines experiential learning as "the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping and transforming experience."
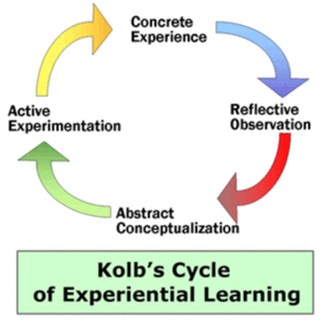
Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory presents a cycle of four elements
Kolb described two different ways of grasping experience:
He also identified two ways of transforming experience:
- Concrete Experience
- Reflective Observation
- Abstract Conceptualization
- Active Experimentation
Kolb described two different ways of grasping experience:
- Concrete Experience
- Abstract Conceptualization
He also identified two ways of transforming experience:
- Reflective Observation
- Active Experimentation
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a dynamic educational approach that emphasizes hands-on, immersive experiences as a primary means of learning. It is rooted in the idea that individuals learn best through direct experiences that engage their senses, emotions, and intellect. Unlike traditional passive learning methods, experiential learning actively involves participants in the learning process, allowing them to apply knowledge in real-world contexts.
This approach to learning is underpinned by the principles of reflection and action. Learners engage in an experience, reflect on the outcomes, and then apply their insights to new situations. This cyclical process enables them to not only acquire knowledge but also develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and emotional intelligence. Experiential learning transcends rote memorization by promoting a deeper understanding of concepts and their practical applications.
Experiential learning can take various forms, including internships, field trips, simulations, case studies, and group projects. These activities provide opportunities for participants to explore, experiment, and collaborate in environments that mirror real-life scenarios. By actively engaging with the subject matter, learners gain firsthand knowledge that is more enduring and transferable than information acquired through passive instruction.
This approach to learning is underpinned by the principles of reflection and action. Learners engage in an experience, reflect on the outcomes, and then apply their insights to new situations. This cyclical process enables them to not only acquire knowledge but also develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and emotional intelligence. Experiential learning transcends rote memorization by promoting a deeper understanding of concepts and their practical applications.
Experiential learning can take various forms, including internships, field trips, simulations, case studies, and group projects. These activities provide opportunities for participants to explore, experiment, and collaborate in environments that mirror real-life scenarios. By actively engaging with the subject matter, learners gain firsthand knowledge that is more enduring and transferable than information acquired through passive instruction.
Experiential Learning Meaning
Experiential learning emphasizes the importance of practical experience in the learning process. It is based on the idea that individuals learn best through hands-on experiences, reflection, and active experimentation. This approach is rooted in the belief that learning is a continuous cycle of experience, reflection, conceptualization, and experimentation, known as the Kolb Experiential Learning Cycle.
Experiential learning is built on the principles of active learning, where learners are actively engaged in the learning process, and learning by doing, where they acquire knowledge and skills through real-world experiences. This was clearly defined in the maxims
I hear and I forget, I see and I remember, I do and I understand. ~ Confucius, 450 BC
Tell me and I forget, Teach me and I remember, Involve me and I will learn. ~ Benjamin Franklin, 1750 A.D
Experiential learning is built on the principles of active learning, where learners are actively engaged in the learning process, and learning by doing, where they acquire knowledge and skills through real-world experiences. This was clearly defined in the maxims
I hear and I forget, I see and I remember, I do and I understand. ~ Confucius, 450 BC
Tell me and I forget, Teach me and I remember, Involve me and I will learn. ~ Benjamin Franklin, 1750 A.D
Experiential Learning Process
The experiential learning process is a cycle of four stages that involve actively engaging with the world to gain new knowledge, skills, and perspectives.
The 4 stage cycle of experiential learning can be repeated continuously, with each new experience building on the previous one and leading to deeper learning and personal growth.
By engaging in the experiential learning process, learners can develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, and decision-making skills, as well as gain practical knowledge and experience.
The 4 stage cycle of experiential learning can be repeated continuously, with each new experience building on the previous one and leading to deeper learning and personal growth.
By engaging in the experiential learning process, learners can develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, and decision-making skills, as well as gain practical knowledge and experience.
Understanding the 4 Stages of Experiential Learning Cycle
1. CONCRETE EXPERIENCE:
Concrete experience describes the hands-on experiences that we learn from. It’s here that we try new things, face problems and step out of our comfort zone. These experiences could be anything in our personal or professional lives. its through experience that we get to learn from our successes or failures.
2. REFLECTIVE OBSERVATION
Next we need to reflect to learn from our experiences. The ‘reflective observation’ phase of the experiential learning cycle is all about reflection on the experiences which include both action and feelings. It’s during this stage that we ponder on the experiences. We get to reflect on what went right and what could be improved? It’s also a chance to observe how it could have been done differently and to learn from each other.
3. ABSTRACT CONCEPTUALIZATION
Once we have identified and understand the defining characteristics of an experience, we can decide on what we can do differently next time. This is a time for planning and brainstorming steps for success.
4. ACTIVE EXPERIMENTATION
The active experimentation phase of the learning cycle is where we get to experiment with our ideas. It’s time to put our plan of action to the test in the real world!
Concrete experience describes the hands-on experiences that we learn from. It’s here that we try new things, face problems and step out of our comfort zone. These experiences could be anything in our personal or professional lives. its through experience that we get to learn from our successes or failures.
2. REFLECTIVE OBSERVATION
Next we need to reflect to learn from our experiences. The ‘reflective observation’ phase of the experiential learning cycle is all about reflection on the experiences which include both action and feelings. It’s during this stage that we ponder on the experiences. We get to reflect on what went right and what could be improved? It’s also a chance to observe how it could have been done differently and to learn from each other.
3. ABSTRACT CONCEPTUALIZATION
Once we have identified and understand the defining characteristics of an experience, we can decide on what we can do differently next time. This is a time for planning and brainstorming steps for success.
4. ACTIVE EXPERIMENTATION
The active experimentation phase of the learning cycle is where we get to experiment with our ideas. It’s time to put our plan of action to the test in the real world!
Examples of Experiential Learning
The experiential learning process does not necessarily begin with experience, however. Instead, each person must choose which learning mode will work best based upon the specific situation. Here is where learning objectives can help the participants achieve a certain desired outcome out of of the process of experiential learning.
For example, let's imagine that you are going to learn how to drive a car. Some people might choose to begin learning via reflection by observing other people as they drive. Another person might prefer to start more abstractly, by reading and analyzing a driving instruction book. Yet another person might decide to just jump right in and get behind the seat of a car to practice driving on a test course.
Below are two experiential learning examples
For example, let's imagine that you are going to learn how to drive a car. Some people might choose to begin learning via reflection by observing other people as they drive. Another person might prefer to start more abstractly, by reading and analyzing a driving instruction book. Yet another person might decide to just jump right in and get behind the seat of a car to practice driving on a test course.
Below are two experiential learning examples
Learning to ride a bicycle:
Learning to coach:
- Reflective observation - Thinking about riding and watching another person ride a bike.
- Abstract conceptualization - Understanding the theory and having a clear grasp of the biking concept.
- Concrete experience - Receiving practical tips and techniques from a biking expert.
- Active experimentation - Leaping on the bike and have a go at it.
Learning to coach:
- Concrete experience - Having a coach guide you in coaching someone else.
- Active experimentation - Using your people skills with what you have learned to achieve your own coaching style.
- Reflective observation - Observing how other people coach.
- Abstract conceptualization - Reading articles to find out the pros and cons of different methods.
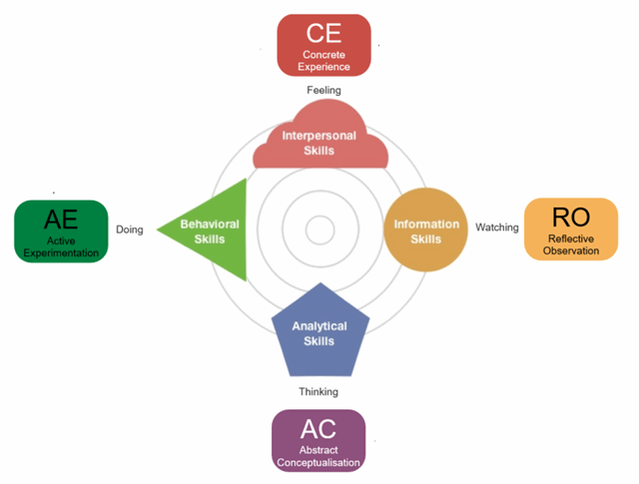
Experiential Learning Styles Model
How do we decide which mode of experiential learning will work best? While situational variables are important, our own preferences play a large role. Kolb notes that people who are considered "watchers" prefer reflective observation, while those who are "doers" are more likely to engage in active experimentation.
"Because of our hereditary equipment, our particular past life experiences, and the demands of our environment, we develop a preferred way of choosing," Kolb explains.
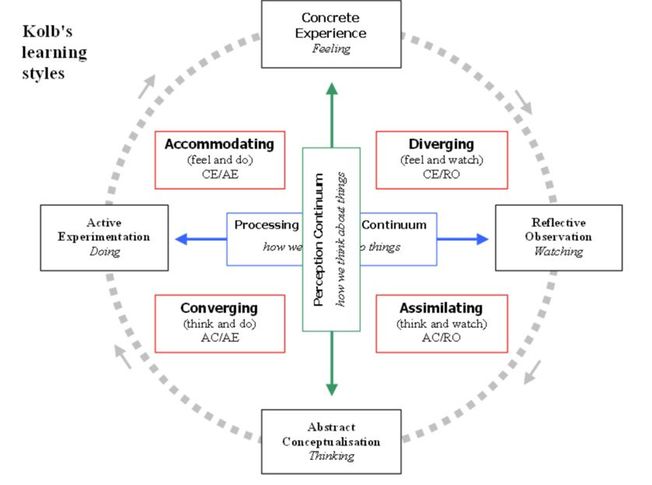
These preferences also serve as the basis for Kolb's learning styles. In this learning style model, each of the four types has dominant learning abilities in two areas.
The four kolb learning styles are
"Because of our hereditary equipment, our particular past life experiences, and the demands of our environment, we develop a preferred way of choosing," Kolb explains.
These preferences also serve as the basis for Kolb's learning styles. In this learning style model, each of the four types has dominant learning abilities in two areas.
The four kolb learning styles are
- Diverging (concrete, reflective) - Emphasizes the innovative and imaginative approach to doing things. Views concrete situations from many perspectives and adapts by observation rather than by action. Interested in people and tends to be feeling-oriented. Likes such activities as cooperative groups and brainstorming.
- Assimilating (abstract, reflective) - Pulls a number of different observations and thoughts into an integrated whole. Likes to reason inductively and create models and theories. Likes to design projects and experiments.
- Converging (abstract, active) - Emphasizes the practical application of ideas and solving problems. Likes decision-making, problem-solving, and the practical application of ideas. Prefers technical problems over interpersonal issues.
- Accommodating (concrete, active) - Uses trial and error rather than thought and reflection. Good at adapting to changing circumstances; solves problems in an intuitive, trial-and-error manner, such as discovery learning. Also tends to be at ease with people.
David Kolb theorized that the four combinations of perceiving and processing determine one of four learning styles of how people prefer to learn. Kolb believes that learning styles are not fixed personality traits, but relatively stable patterns of behavior that is based on their background and experiences.
What is both interesting and important for group work is that different people tend to have different styles of learning, and therefore, place more emphasis, or feel more comfortable, in some stages of the learning cycle than others.
The learning styles are combinations of the individual’s preferred approaches. These learning styles are as follows:
- Reflector / Diverger
- Theorist / Assimilator
- Pragmatist / Converger
- Activist / Accomodator
For example, people with the Diverging learning style are dominant in the areas of concrete experience and reflective observation.
Kolb suggests that a number of different factors can influence preferred learning styles. Some of the factors that he has identified include:
- Personality type
- Educational specialization
- Career choice
- Current job role
- Adaptive competencies
How to find ones Kolbs Learning Style
Knowing participants learning styles enables educators to design learning experiences that are orientated to the preferred method.
In a real world scenario everyone responds to and requires the stimulus of all types of learning styles to one extent or another. it's a matter of focusing on methods that best enable learning in the given context, situation and a person's learning style preference.
The kolb learning style inventory is a great instrument to discover your learning styles.
In a real world scenario everyone responds to and requires the stimulus of all types of learning styles to one extent or another. it's a matter of focusing on methods that best enable learning in the given context, situation and a person's learning style preference.
The kolb learning style inventory is a great instrument to discover your learning styles.
Experiential learning and reflection
Reflection is the cornerstone of experiential learning. It's the crucial step that takes an experience from a fleeting event to a meaninful understanding. Through reflection, learners aren't simply recalling facts, they're actively dissecting their experience. They're analyzing successes and failures, connecting the experience to existing knowledge, and most importantly, identifying how these learnings can be applied in the future.
It's not enough to simply participate in activities; true learning happens when learners take a step back to analyze their experiences. This involves describing what happened and their emotional response, then dissecting the experience to identify strengths and weaknesses. The magic happens when learners connect the experience to existing knowledge, drawing parallels and building a web of understanding.
This process of reflection transforms experience into transferable skills and fosters a deeper understanding that traditional learning methods often struggle to achieve. Through reflection, learners don't just acquire information; they internalize it, transforming experiences into valuable building blocks for lifelong learning. The process of reflection empowers learners to not just experience, but to truly learn and grow.
It's not enough to simply participate in activities; true learning happens when learners take a step back to analyze their experiences. This involves describing what happened and their emotional response, then dissecting the experience to identify strengths and weaknesses. The magic happens when learners connect the experience to existing knowledge, drawing parallels and building a web of understanding.
This process of reflection transforms experience into transferable skills and fosters a deeper understanding that traditional learning methods often struggle to achieve. Through reflection, learners don't just acquire information; they internalize it, transforming experiences into valuable building blocks for lifelong learning. The process of reflection empowers learners to not just experience, but to truly learn and grow.
Reflection techniques in experiential learning
Experiential learning thrives on a variety of reflection techniques, catering to different learning styles and fostering deeper engagement. Here's a glimpse into some popular methods:
Individual Reflection Techniques
Individual Reflection Techniques
- Journaling: This classic method allows learners to delve into their inner world. By writing down thoughts and feelings after an experience, learners solidify memories, identify emotions, and gain clarity on what transpired.
- Freewriting: For those who prefer a stream-of-consciousness approach, freewriting encourages writing continuously for a set time without stopping or editing. This can unearth hidden insights and connections.
- One-word Check-in: Participants share one word that encapsulates their feelings or thoughts about the experience. This technique encourages brevity and can quickly gauge the overall mood of the group.
- One-Sentence Debrief: This technique is a quick and easy way to get a sense of participants' key takeaways from the experience. The facilitator simply asks each participant to share one sentence that summarizes their learning.
Visual Reflection Techniques
Here Participants use visual aids such as drawings, diagrams, or mind maps to represent their thoughts, emotions, and insights from the experience. This hands-on approach can stimulate creativity and deeper reflection.
Here Participants use visual aids such as drawings, diagrams, or mind maps to represent their thoughts, emotions, and insights from the experience. This hands-on approach can stimulate creativity and deeper reflection.
- Mind Mapping: Visual learners can create a visual representation of the experience, with key concepts and connections branching out from a central theme. This helps identify patterns, relationships, and key takeaways.
- Concept Maps: Similar to mind maps, concept maps focus on establishing relationships between ideas. Learners can use arrows and labels to show how different aspects of the experience connect.
- Photographic Reflection: Taking pictures throughout the experience allows learners to revisit key moments later for reflection. Photos can spark memories, trigger emotions, and provide a springboard for deeper analysis
- Gallery Walk: In a gallery walk, participants create posters or other visual representations of their experience. Then, they walk around the room and look at each other's work. This can be a great way to spark conversation and help participants to see the experience from different perspectives
Group Reflection Techniques
- Group Discussions: Sharing experiences with peers fosters a collaborative learning environment. Discussions spark new perspectives, encourage analysis from different angles, and solidify learning through explanation and debate.
- Role Reversal: Participants take on the perspective of another person involved in the experience, such as a colleague or a client. This technique promotes empathy and a deeper understanding of different viewpoints. for example Flip Flop Method
- Sharing Circles: This is a classic technique where participants gather in a circle and take turns sharing their thoughts and feelings about the experience. The facilitator can ask guiding questions to help keep the discussion focused and on point.
- Pair and Share: This technique is similar to sharing circles, but it allows for more focused conversation. Participants are paired up and asked to discuss a specific question or aspect of the experience with their partner. Then, the pairs can come back together as a large group and share what they discussed.
- Gestalt Approach: What - So What - Now What - Participants focus on specific elements of the experience, such as interactions with others or personal reactions, and explore them in depth to gain insight into their behavior and motivations.
- Asking Questions as per the 4 steps of experiential learning cycle.
- Structured Group Discussion: Facilitators guide participants through a structured discussion focusing on specific aspects of the experience, such as emotions, challenges faced, successes achieved, and lessons learned. for example ORID reflection method, Gibbs' Reflective Cycle, 4F reflection method (Facts, Feelings, Findings, and Future)
- Facilitator Observations: Sharing facilitators observations and asking participants to revist the experience and reflect on insights and different ways of doing things in future.
- Role-Playing Debriefings: After an activity involving role-playing, have participants switch roles and re-enact the scenario. This allows learners to see things from a different viewpoint and gain a deeper understanding of the experience.
- Timeline Reflection: Participants create a timeline of the experience, marking significant events and their emotional responses at different points. This visual representation helps identify patterns and transitions.
- SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats): Participants identify strengths and weaknesses of their actions during the experience, opportunities for improvement, and potential threats or obstacles to success in future endeavors.
- Appreciative Inquiry: Participants reflect on positive aspects of the experience, identifying what worked well and how those successes can be applied in the future. This approach emphasizes strengths and encourages optimism.
- Fishbowl Technique: A small group of participants sits in a circle to discuss their experiences while the larger group observes silently. After a set time, the observers join the discussion, providing different perspectives.
Creative Expression Methods
- Artistic Expression: For some, words fall short. Expressing the experience through drawing, painting, or even music can be a powerful tool. This approach allows for a more personal and emotional connection to the learning.
- Storytelling: Crafting a narrative around the experience can help learners identify a beginning, middle, and end, fostering a sense of structure and purpose. Stories can be shared verbally, written down, or even performed.
- Applying Metaphors: Participants use metaphors or analogies to describe their experiences, making connections between the experiential activity and real-life situations. This technique encourages abstract thinking and creativity. for example using a tree as a metophor.
Characteristics of experiential learning
Experiential learning is characterized by several key elements that distinguish it from traditional forms of education. These characteristics play a crucial role in unlocking the potential of learners and maximizing their learning outcomes.
1. Hands-on activities: Experiential learning involves actively engaging with the subject matter through hands-on activities. This could include experiments, simulations, field trips, or real-world projects. By directly interacting with the material, learners are able to deepen their understanding and develop practical skills.
2. Reflection: Reflection is an integral part of the experiential learning process. Learners are encouraged to reflect on their experiences, examine the outcomes, and analyze the lessons learned. This reflection process enhances self-awareness, promotes personal growth, and provides valuable insights for future decision-making.
3. Active engagement: Experiential learning encourages learners to actively participate, collaborate, and experiment. By doing so, they gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and develop practical skills that can be immediately implemented. This active engagement promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts.
4. Real-world relevance: Experiential learning emphasizes the application of knowledge in real-world contexts. By engaging with authentic scenarios, learners can see the practical relevance of their learning. This not only enhances their understanding but also prepares them for real-life challenges.
5. Learner-centered: Experiential learning is learner-centered, focusing on the individual needs and interests of each learner. It recognizes that individuals have different learning styles and preferences, and therefore offers a variety of activities to cater to these diverse needs. learners learn through various expereinces and learning orientations and includes the kinesthetic learners, the auditory learners and the visual learners
1. Hands-on activities: Experiential learning involves actively engaging with the subject matter through hands-on activities. This could include experiments, simulations, field trips, or real-world projects. By directly interacting with the material, learners are able to deepen their understanding and develop practical skills.
2. Reflection: Reflection is an integral part of the experiential learning process. Learners are encouraged to reflect on their experiences, examine the outcomes, and analyze the lessons learned. This reflection process enhances self-awareness, promotes personal growth, and provides valuable insights for future decision-making.
3. Active engagement: Experiential learning encourages learners to actively participate, collaborate, and experiment. By doing so, they gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and develop practical skills that can be immediately implemented. This active engagement promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts.
4. Real-world relevance: Experiential learning emphasizes the application of knowledge in real-world contexts. By engaging with authentic scenarios, learners can see the practical relevance of their learning. This not only enhances their understanding but also prepares them for real-life challenges.
5. Learner-centered: Experiential learning is learner-centered, focusing on the individual needs and interests of each learner. It recognizes that individuals have different learning styles and preferences, and therefore offers a variety of activities to cater to these diverse needs. learners learn through various expereinces and learning orientations and includes the kinesthetic learners, the auditory learners and the visual learners
Benefits and Importance of Experiential Learning
The benefits of experiential learning are multifaceted and extend across diverse domains, including education, professional development, and personal growth. For learners, the hands-on nature of experiential learning promotes deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. By actively participating in activities that directly relate to the subject matter, they can internalize concepts and apply them in practical situations.
Experiential learning promotes the development of essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and teamwork. Through real-world experiences, individuals can hone these skills in authentic contexts, preparing them for success in academic, professional, and personal pursuits. Additionally, experiential learning nurtures a sense of autonomy and self-efficacy, empowering learners to take ownership of their learning journey.
For educators and employers, experiential learning offers insights into the capabilities and potential of individuals. By observing how learners navigate challenges and collaborate with others in experiential activities, educators and employers can gain a holistic understanding of their strengths, areas for growth, and learning styles.
Some of the many benefits of experiential learning are:
Experiential learning promotes the development of essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and teamwork. Through real-world experiences, individuals can hone these skills in authentic contexts, preparing them for success in academic, professional, and personal pursuits. Additionally, experiential learning nurtures a sense of autonomy and self-efficacy, empowering learners to take ownership of their learning journey.
For educators and employers, experiential learning offers insights into the capabilities and potential of individuals. By observing how learners navigate challenges and collaborate with others in experiential activities, educators and employers can gain a holistic understanding of their strengths, areas for growth, and learning styles.
Some of the many benefits of experiential learning are:
- Makes learning relatable to participants: Participants build on what they already know and are provided with opportunities to make connections between new concepts and existing ones.
- Increases the effectiveness of learning: Participants engage in critical thinking, acquire problem solving skills and engage in decision making.
- Links theory to practice: Participants have the chance to engage in the experience and practice what they have learned, see the application of the theoretical concepts in practice, process that application and make generalizations.
- Increases Participants’ engagement, by encouraging collaboration and scaffolding between learners.
- Assists in memory retention, by building strong relationships between feelings and thinking processes. Participants have the capacity to learn successfully when the information is associated with values and feelings.
- Leads to development of skills for lifelong learning, by assisting in the acquisition of essential skills and encouraging Participants to reflect, conceptualize, and plan for next steps.
Principles of Experiential Learning
1. The learner has a real authentic experience which includes real consequences where the experiential learner makes a choice to participate and is intentionally involved in examining ,exploring and playing with a real world experience that can lead to any outcome.
2. The experience is an hands-on "feeling and doing" interaction. The experience can be planned or be completely spontaneous. There is very less or no teaching involved and the experience may include experiences which involve solo and group involvement.
3. The experience is direct experience with focused reflection and builds on past knowledge and experiences. It requires active involvement in construction of meaning and encourages collaboration and exchange of ideas and perspectives between the participants.
4. The learner actively reflects on that experience through individual thought, group discussion, questioning, processing or writing in a journal. They may participate in group processing and discussion including debriefing and reflective questions posed by a facilitator who challenges the group to create personal meaning and transference of learning to new situations.
5. The Learning is able to draw conclusions and makes sense of what the learner has experienced, including having opportunities to relate this/ her own experiences with those of others. The learner may develop theories, models or concepts about the experience. The learner may develop new questions, which can lead to the next experience or explorations. The learner is able to apply their new learned knowledge in the next experiences.
2. The experience is an hands-on "feeling and doing" interaction. The experience can be planned or be completely spontaneous. There is very less or no teaching involved and the experience may include experiences which involve solo and group involvement.
3. The experience is direct experience with focused reflection and builds on past knowledge and experiences. It requires active involvement in construction of meaning and encourages collaboration and exchange of ideas and perspectives between the participants.
4. The learner actively reflects on that experience through individual thought, group discussion, questioning, processing or writing in a journal. They may participate in group processing and discussion including debriefing and reflective questions posed by a facilitator who challenges the group to create personal meaning and transference of learning to new situations.
5. The Learning is able to draw conclusions and makes sense of what the learner has experienced, including having opportunities to relate this/ her own experiences with those of others. The learner may develop theories, models or concepts about the experience. The learner may develop new questions, which can lead to the next experience or explorations. The learner is able to apply their new learned knowledge in the next experiences.
Why Organisations are Employing Experiential Learning
The idea of experiential learning isn't entirely new. Management Guru Henry Mintzberg pointed out long ago that, "leadership, like swimming, cannot be learned by reading about it".
A lot about learning is about mindset, and one of the fastest change the mindset is to come out of the comfort zone in a different learning environment that experiential learning provides.
In the professional realm, experiential learning serves as a catalyst for continuous growth and skill development. Employers can harness the power of experiential learning to cultivate a culture of innovation, adaptability, and continuous improvement within their organizations. By providing employees with opportunities to engage in hands-on experiences, employers can nurture a workforce that is agile, creative, and adept at tackling real-world challenges.
One effective approach to implementing experiential learning in the workplace is through immersive training programs. Instead of relying solely on traditional classroom-style training, organizations can design experiential learning experiences that simulate work environments and scenarios. This type of training allows employees to practice new skills, make decisions, and receive immediate feedback in a controlled yet realistic setting.
A lot about learning is about mindset, and one of the fastest change the mindset is to come out of the comfort zone in a different learning environment that experiential learning provides.
In the professional realm, experiential learning serves as a catalyst for continuous growth and skill development. Employers can harness the power of experiential learning to cultivate a culture of innovation, adaptability, and continuous improvement within their organizations. By providing employees with opportunities to engage in hands-on experiences, employers can nurture a workforce that is agile, creative, and adept at tackling real-world challenges.
One effective approach to implementing experiential learning in the workplace is through immersive training programs. Instead of relying solely on traditional classroom-style training, organizations can design experiential learning experiences that simulate work environments and scenarios. This type of training allows employees to practice new skills, make decisions, and receive immediate feedback in a controlled yet realistic setting.
Educators are now coming round to the notion of integrating experiential learning as a complement to the classroom training. Facilitators are designing and delivering behavioral skills training using experiential learning methods.
When Does Experiential Learning Happen
Experiential learning is said to happen or take place when participants get immersed cognitively, emotionally , behaviorally and are supported by a facilitator in reflecting, processing the experiences, emotions, thoughts, and actions to get a insight in a safe learning environment, leading to change in perspective, understanding, thought, and behavior. An important aspect of experiential learning is transference, where the participants are able to apply the newly acquired learning in a different real life situation thereby demonstrating change.
How is experiential learning delivered
Training needs and desired outcomes are identified, conducive and safe learning environment away from work is created and participants are walked through a sequence of activities that focus on ice breaking, energizing, trusting building initially.
Once participants are engaged and feel safe, they are put into various tasks and challenges where they get to participate in a experience.
The sequence of the tasks or activities follows low order thinking skills to high order thinking skills. After every activity the facilitator invites the participants to take part in in a discussion where the facilitator debriefs or processes the experiences.
The facilitator invites the group to achieve a goal, but does not explain how to successfully complete the activity. Participants must work to discover solutions individually and together as a team, and must communicate and learn from each other in order to be successful.
The Learning begins with the experience followed by reflection, discussion, analysis and evaluation of the experience.
Once participants are engaged and feel safe, they are put into various tasks and challenges where they get to participate in a experience.
The sequence of the tasks or activities follows low order thinking skills to high order thinking skills. After every activity the facilitator invites the participants to take part in in a discussion where the facilitator debriefs or processes the experiences.
The facilitator invites the group to achieve a goal, but does not explain how to successfully complete the activity. Participants must work to discover solutions individually and together as a team, and must communicate and learn from each other in order to be successful.
The Learning begins with the experience followed by reflection, discussion, analysis and evaluation of the experience.
How do participants learn in Experiential learning
The Participants undergoing the experience are instantly able to feel the results of their actions by participating in the experience. During the processing they get to realize the immense difference that can be made by a changing their thinking and behavior to the real life application.
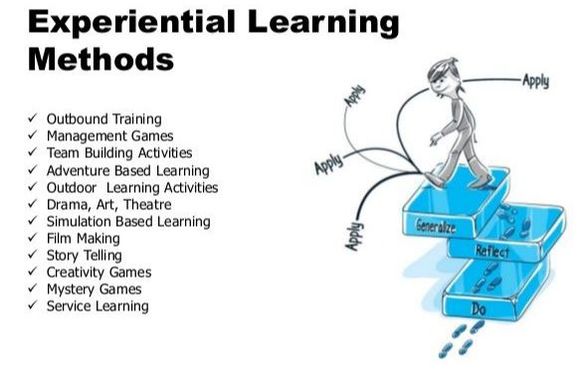
Where can Experiential Learning can be used
Experiential learning can become a continuous process of learning and development in corporate companies and schools by adopting the basic steps of "do, reflect and apply".
There are many ways to practice these experiential learning techniques some of which are outlined below.
There are many ways to practice these experiential learning techniques some of which are outlined below.
Outbound Training
Virtual Online Team Building
Management Games
Team Building Activities
Adventure Based Learning
Gamed Based Learning
Outdoor Learning Activities
Inhouse Learning Activities
Drama, Art, Theatre
Simulation Based Learning
Film Making
Story Telling
Creativity Games
Mystery Games
Service Learning
What do Participants Feel in Experiential Learning Programs
|
The Participants undergoing the experience are instantly able to feel the results of their actions by participating in the experience. They get emotionally engaged and involved. This makes them open to reflection and introspection. During the processing of the experience with the facilitator they get to realize the immense difference that can be made by a changing their thinking and behavior to better ways of performing as an individual or as a team
|
What are Application Areas of Experiential Learning
A range of abstract concepts, skills and behaviors can be learned with experiential learning. It's more effective with change in human behavior and attitude than technical knowledge. Experiential learning is impact in most learning scenarios and can be delivered through education, facilitation and self participatory methods.
|
Team Building
Team Bonding Trust Building Collaboration Communication Motivating Teams Assertiveness Decision Making Innovation Strategic Thinking Creativity Customer Focus Confidence Building Conflict Management Management Development |
Leadership Development Programs
Change Management Cross Functional Teams Cross Cultural Teams Virtual Teams High Performance Teams Coaching Mentoring Organizational effectiveness Thought Leadership Conflict Management Time Management Stress Management Emotional Intelligence Goal Setting |
What is Experimental Learning
Experimental learning is a structured learning process through direct experience, observation, and reflection. It involves:
In Experimental learning, learners are encouraged to explore, question, and experiment with different ideas and concepts. The goal is to help learners gain a deeper understanding of the material by putting it into practice and experiencing it firsthand.
Experimental learning can take many forms, such as project-based learning, field trips, simulations, role-playing, and laboratory experiments. It is often used in scientific and technical fields but can be applied to any other subject or discipline.
- Actively engaging in an experience that has a scientific method, technical or experimental design.
- Reflecting on what happened during the experience.
- Drawing inferences from that reflection.
In Experimental learning, learners are encouraged to explore, question, and experiment with different ideas and concepts. The goal is to help learners gain a deeper understanding of the material by putting it into practice and experiencing it firsthand.
Experimental learning can take many forms, such as project-based learning, field trips, simulations, role-playing, and laboratory experiments. It is often used in scientific and technical fields but can be applied to any other subject or discipline.
Difference between Experimental Learning and Experiential Learning
Experimental learning and experiential learning are similar in that they both involve learning through direct experience. However, there are some subtle differences between the two.
Experimental learning typically involves a more structured and systematic approach to learning. It often involves designing and carrying out experiments to test hypotheses or theories. This type of learning is commonly used in scientific research and technical fields.
On the other hand, experiential learning is a broader term encompassing a range of learning experiences, including but not limited to experimental learning. Experiential learning can involve any direct experience that allows learners to reflect on their experiences and develop new knowledge and skills.
Overall, while experimental learning is a specific type of experiential learning, experiential learning encompasses a broader range of learning experiences that go beyond the scientific method and experimental design.
Experimental learning typically involves a more structured and systematic approach to learning. It often involves designing and carrying out experiments to test hypotheses or theories. This type of learning is commonly used in scientific research and technical fields.
On the other hand, experiential learning is a broader term encompassing a range of learning experiences, including but not limited to experimental learning. Experiential learning can involve any direct experience that allows learners to reflect on their experiences and develop new knowledge and skills.
Overall, while experimental learning is a specific type of experiential learning, experiential learning encompasses a broader range of learning experiences that go beyond the scientific method and experimental design.
Technology and experiential learning
Technology plays a pivotal role in advancing the frontiers of experiential learning. With the advent of virtual reality, augmented reality, and simulation software, learners can access immersive learning experiences that were once confined to physical settings. Virtual simulations allow learners to engage in realistic scenarios, such as medical procedures, engineering designs, and environmental simulations, without the constraints of physical resources.
Furthermore, interactive digital platforms facilitate collaborative experiential learning experiences that transcend geographical boundaries. Through online simulations, virtual team projects, and interactive case studies, learners can engage with peers and mentors from diverse backgrounds, building a global perspective and cross-cultural understanding. Technology-enabled experiential learning also promotes inclusivity and accessibility, as individuals can participate in activities regardless of their physical location.
While technology enhances the reach and scope of experiential learning, it is important to maintain a balance between digital experiences and tangible, real-world interactions. Combining virtual simulations with hands-on experiences ensures that learners benefit from diverse modes of experiential learning, catering to different learning styles and preferences. By integrating technology judiciously, educators and employers can create multifaceted experiential learning ecosystems that embrace innovation and inclusivity.
Furthermore, interactive digital platforms facilitate collaborative experiential learning experiences that transcend geographical boundaries. Through online simulations, virtual team projects, and interactive case studies, learners can engage with peers and mentors from diverse backgrounds, building a global perspective and cross-cultural understanding. Technology-enabled experiential learning also promotes inclusivity and accessibility, as individuals can participate in activities regardless of their physical location.
While technology enhances the reach and scope of experiential learning, it is important to maintain a balance between digital experiences and tangible, real-world interactions. Combining virtual simulations with hands-on experiences ensures that learners benefit from diverse modes of experiential learning, catering to different learning styles and preferences. By integrating technology judiciously, educators and employers can create multifaceted experiential learning ecosystems that embrace innovation and inclusivity.
Challenges in the field of expereintail learning
Despite its transformative potential, experiential learning is not without its challenges. Implementing experiential learning initiatives may require significant resources, time, and logistical coordination. Educators and employers may encounter resistance to change or skepticism about the effectiveness of hands-on learning approaches. Furthermore, assessing the impact of experiential learning activities and measuring learning outcomes can present inherent complexities.
To address these challenges, proactive planning and stakeholder engagement are essential. Educators and employers should articulate the value proposition of experiential learning, emphasizing its capacity to build critical skills, adaptability, and real-world relevance. By aligning experiential learning initiatives with strategic objectives and demonstrating their tangible benefits, stakeholders can be inspired to support and invest in these transformative learning approaches.
Additionally, leveraging partnerships with community organizations, industry stakeholders, and technology providers can enhance the scalability and sustainability of experiential learning initiatives. Collaborative efforts can expand access to resources, expertise, and diverse learning opportunities, enriching the experiential learning ecosystem. By building a network of support and collaboration, educators and employers can overcome logistical challenges and amplify the impact of experiential learning.
To address these challenges, proactive planning and stakeholder engagement are essential. Educators and employers should articulate the value proposition of experiential learning, emphasizing its capacity to build critical skills, adaptability, and real-world relevance. By aligning experiential learning initiatives with strategic objectives and demonstrating their tangible benefits, stakeholders can be inspired to support and invest in these transformative learning approaches.
Additionally, leveraging partnerships with community organizations, industry stakeholders, and technology providers can enhance the scalability and sustainability of experiential learning initiatives. Collaborative efforts can expand access to resources, expertise, and diverse learning opportunities, enriching the experiential learning ecosystem. By building a network of support and collaboration, educators and employers can overcome logistical challenges and amplify the impact of experiential learning.
Experiential Learning Implications for Educators.
Knowing a participants (and your educators) learning style enables learning experiences to be designed according to the preferred learning style.
Both Kolb's learning styles and experiential learning model can be used by educators to design learning experiences that are emotionally engaging, immersive and closer to real life applications.
Educators should ensure that the experiential learning activities are designed and carried out in ways that offer each learner the chance to engage in the manner that suits them best as per their preferred learning styles.
Educators can support participants to learn more efficiently and effectively by combining learning styles with the learning cycle helping educators to target more specific learning sessions for the participants. Educators can design learning exercises that relate with the way participants take in information and tailor the learning intervention that is in line with kolbs four stages.
By providing different learning initiatives, we increase the chances of the person assimilating the information effectively and helping them develop insights that may have been out of their capability if the learning had been in a different style.
In a real world scenario, activities and learning experiences should be developed in ways that build up on each stage of the experiential learning cycle and take the participants through the whole process in sequence make it a wholesome learning experience.
Both Kolb's learning styles and experiential learning model can be used by educators to design learning experiences that are emotionally engaging, immersive and closer to real life applications.
Educators should ensure that the experiential learning activities are designed and carried out in ways that offer each learner the chance to engage in the manner that suits them best as per their preferred learning styles.
Educators can support participants to learn more efficiently and effectively by combining learning styles with the learning cycle helping educators to target more specific learning sessions for the participants. Educators can design learning exercises that relate with the way participants take in information and tailor the learning intervention that is in line with kolbs four stages.
By providing different learning initiatives, we increase the chances of the person assimilating the information effectively and helping them develop insights that may have been out of their capability if the learning had been in a different style.
In a real world scenario, activities and learning experiences should be developed in ways that build up on each stage of the experiential learning cycle and take the participants through the whole process in sequence make it a wholesome learning experience.
Designing effective experiential learning activities
The design of effective experiential learning activities is a critical factor in maximizing the impact of this educational approach. When crafting experiential learning experiences, it is essential to align the activities with specific learning objectives and desired outcomes. This deliberate approach ensures that the experiences are purposeful and contribute to the development of targeted skills and knowledge.
Furthermore, experiential learning activities should be structured to promote active engagement and reflection. Participants should have opportunities to explore, experiment, and collaborate in ways that challenge their assumptions and encourage them to think critically. By incorporating elements of inquiry-based learning and problem-based learning, experiential activities can spark curiosity, build independent thinking, and inspire innovative solutions.
The integration of technology can also enhance the effectiveness of experiential learning activities. Virtual reality simulations, interactive learning platforms, and digital collaboration tools can provide immersive and interactive experiences that transcend physical limitations. By leveraging technology, educators and employers can create dynamic experiential learning environments that mirror real-world challenges and opportunities.
Furthermore, experiential learning activities should be structured to promote active engagement and reflection. Participants should have opportunities to explore, experiment, and collaborate in ways that challenge their assumptions and encourage them to think critically. By incorporating elements of inquiry-based learning and problem-based learning, experiential activities can spark curiosity, build independent thinking, and inspire innovative solutions.
The integration of technology can also enhance the effectiveness of experiential learning activities. Virtual reality simulations, interactive learning platforms, and digital collaboration tools can provide immersive and interactive experiences that transcend physical limitations. By leveraging technology, educators and employers can create dynamic experiential learning environments that mirror real-world challenges and opportunities.
How Corporate Companies can use Experiential Learning for training employees
Every organization is unique in its training needs, and therefore each company will likely have their own way of implementing experiential learning strategies. However, here are some activities and approaches that you can consider when tailoring your own experiential learning initiatives:
1) Team Building: Team building is a widely used group-development activity in organizations. Team building activities are better suited for cooperative and collaborative behaviors for cross-functional teams, so they develop actions that can support collaborative functioning. it is often used to enhance interdependence and define roles within teams, often involving cooperative and collaborative tasks.
Learn More on Team Building
2. Outbound Training
OBT Training or Outbound Training is an evidence-based training method for enhancing employee and team performance through outdoor, adventure, and challenging group activities designed around experiential learning and run in an offsite environment
The outbound approach is based on Outward Bound method of group development through outdoor group activities that focus on tackling challenging scenarios in the outdoors and involve problem-solving, decision making, communication, and risk-taking. Participants face real consequences and develop the ability to adapt, grow, and succeed as teams.
Learn more on Outbound Training
3. Business Simulations: This experiential training technique uses electronic, mechanical or software-based activities to simulate a real-world situation to which a learner must react. Since the simulations can vary depending on any number of parameters, simulated training offers a great way to educate staff on even the most remote hypothetical scenarios that they might have to deal with.
4. Case Studies: These are great examples of experiential learning that are based on real-life instances, situations that have transpired in the past. By exposing trainees to what happened in the past, using illustrative case studies, trainers can give them invaluable insight into the appropriate behavior required to deal with similar situations, and the blow-back it may have.
5. Role Playing: These are experiential training activities designed to help employees appreciate specific work situations from perspectives different than their own. For instance, a Customer Service manager might play the role of a customer, in order to experience the impact that a particular policy or procedure might have on the customer.
6. Sensitivity Training: One highly effective experiential training strategy to enhance employee self-awareness and confidence is sensitivity training. The objective is to design activities that help learners appreciate how others (peers, managers, customers) see them. As a result, workers become equipped with the skills and knowledge of how to deal with others more appropriately.
7. Gaming: Experiential learning games are a popular way to help employees learn by doing. The games can be organized in a way that individuals and groups play with each other, by either collaborating or competing, like in the real world. This process can teach them valuable lessons about how to deal with on-the-job situations. As part of this experiential training technique, motivation tools, such as points and merit badges, can be awarded to make the game more engaging for the learners.
Learn more on Online Game Based Experiential Learning
8. On Job Training (OJT): Of all the experiential learning strategies out there, OJT is probably the one that offers the most realistic training experience. By designing experiential activities for groups of trainees, based at the actual location where they will be working, OJT exposes staff to “business as usual” situations – real customers, peers, and supervisors, real products, and services – that they will continue to deal with once training is completed.
1) Team Building: Team building is a widely used group-development activity in organizations. Team building activities are better suited for cooperative and collaborative behaviors for cross-functional teams, so they develop actions that can support collaborative functioning. it is often used to enhance interdependence and define roles within teams, often involving cooperative and collaborative tasks.
Learn More on Team Building
2. Outbound Training
OBT Training or Outbound Training is an evidence-based training method for enhancing employee and team performance through outdoor, adventure, and challenging group activities designed around experiential learning and run in an offsite environment
The outbound approach is based on Outward Bound method of group development through outdoor group activities that focus on tackling challenging scenarios in the outdoors and involve problem-solving, decision making, communication, and risk-taking. Participants face real consequences and develop the ability to adapt, grow, and succeed as teams.
Learn more on Outbound Training
3. Business Simulations: This experiential training technique uses electronic, mechanical or software-based activities to simulate a real-world situation to which a learner must react. Since the simulations can vary depending on any number of parameters, simulated training offers a great way to educate staff on even the most remote hypothetical scenarios that they might have to deal with.
4. Case Studies: These are great examples of experiential learning that are based on real-life instances, situations that have transpired in the past. By exposing trainees to what happened in the past, using illustrative case studies, trainers can give them invaluable insight into the appropriate behavior required to deal with similar situations, and the blow-back it may have.
5. Role Playing: These are experiential training activities designed to help employees appreciate specific work situations from perspectives different than their own. For instance, a Customer Service manager might play the role of a customer, in order to experience the impact that a particular policy or procedure might have on the customer.
6. Sensitivity Training: One highly effective experiential training strategy to enhance employee self-awareness and confidence is sensitivity training. The objective is to design activities that help learners appreciate how others (peers, managers, customers) see them. As a result, workers become equipped with the skills and knowledge of how to deal with others more appropriately.
7. Gaming: Experiential learning games are a popular way to help employees learn by doing. The games can be organized in a way that individuals and groups play with each other, by either collaborating or competing, like in the real world. This process can teach them valuable lessons about how to deal with on-the-job situations. As part of this experiential training technique, motivation tools, such as points and merit badges, can be awarded to make the game more engaging for the learners.
Learn more on Online Game Based Experiential Learning
8. On Job Training (OJT): Of all the experiential learning strategies out there, OJT is probably the one that offers the most realistic training experience. By designing experiential activities for groups of trainees, based at the actual location where they will be working, OJT exposes staff to “business as usual” situations – real customers, peers, and supervisors, real products, and services – that they will continue to deal with once training is completed.
How Schools and Education Institutes can use experiential learning opportunities for teaching?
In educational settings, the integration of experiential learning can enrich traditional curricula and invigorate the learning experience for students. Educators can leverage experiential learning to bridge the gap between theory and practice, enabling students to contextualize academic concepts in real-world scenarios. This approach not only enhances learning engagement but also cultivates a deeper appreciation for the relevance and applicability of academic knowledge.
An example of experiential learning in education is the use of service-learning projects. By engaging in community service activities that align with academic objectives, students can apply their learning to address real community needs. This not only reinforces their understanding of course content but also instills a sense of civic responsibility and empathy. Moreover, service-learning projects nurture a spirit of collaboration and social awareness, equipping students with valuable life skills beyond the classroom.
Effective application of experiential learning in educational settings is through interactive simulations and role-playing exercises. These immersive activities enable students to step into different roles, navigate complex scenarios, and make decisions with consequences. By experiencing the outcomes of their choices firsthand, students gain practical insights and emotional connections to the subject matter, building a deeper understanding of complex concepts where learners learn through involement and engagement irrespective of the type of of learner one is.
An example of experiential learning in education is the use of service-learning projects. By engaging in community service activities that align with academic objectives, students can apply their learning to address real community needs. This not only reinforces their understanding of course content but also instills a sense of civic responsibility and empathy. Moreover, service-learning projects nurture a spirit of collaboration and social awareness, equipping students with valuable life skills beyond the classroom.
Effective application of experiential learning in educational settings is through interactive simulations and role-playing exercises. These immersive activities enable students to step into different roles, navigate complex scenarios, and make decisions with consequences. By experiencing the outcomes of their choices firsthand, students gain practical insights and emotional connections to the subject matter, building a deeper understanding of complex concepts where learners learn through involement and engagement irrespective of the type of of learner one is.
There are many ways in which schools can use experiential learning opportunities by having students actively engaged in hands-on learning and enhance teaching excellence and student success.
- Mock-trials or debates
- Organizing business internships.
- School camps or a boarding component to campus life; here, students are responsible for some aspects of their daily life such as cleaning, time management and study
- Undertaking drills to develop specific physical skills
- Community service opportunities, such as work trips to support disadvantaged communities
- Study tours to international universities where students experience on-campus life and undertake undergraduate study
- Every film or novel study in English, where a student enters the world of the story and lingers on the complexities of the perspective of the protagonist
- Simulations, such as in a Business Studies class examining the factors behind stock market fluctuations
- Scientific experiments or open-ended inquiries to determine cause and effect
- Case studies of urban development in Geography
- Role-playing influential historical figures in order to understand personal motivations in a History class
- Interactive classroom games, such as Kahoot or Socrative
- Outdoor and Adventure Camps
Taking it forward
When deciding which of these methods, styles and activities you should use, it is vital to not lose focus of what the central idea of experiential training is all about: Learning by doing. So, if your specific training needs aren’t in alignment with a particular technique discussed above, you shouldn’t attempt to “force fit” it into your training strategy.
Experiential learning represents a paradigm shift in the realm of education and professional development. By immersing participants in real-world experiences, building critical skills, and embracing innovative technologies, experiential learning unlocks boundless opportunities for growth and advancement. Educators, employers, and individuals alike can harness the transformative power of experiential learning to cultivate resilient, adaptable, and agile learners who are primed for success in a rapidly evolving world.
As you embark on your journey to integrate experiential learning into your educational or professional endeavors, remember that the keys to unlocking its power lie in intentional design, reflective practice, and a commitment to inclusive and impactful learning experiences. By embracing experiential learning as a catalyst for continuous growth and learning, you are poised to revolutionize the way knowledge is acquired, applied, and shared, shaping a future where experiential learning propels individuals and organizations toward unparalleled heights of achievement and innovation.
For Consultation for your experiential learning needs please get in touch with us at [email protected]
Experiential learning represents a paradigm shift in the realm of education and professional development. By immersing participants in real-world experiences, building critical skills, and embracing innovative technologies, experiential learning unlocks boundless opportunities for growth and advancement. Educators, employers, and individuals alike can harness the transformative power of experiential learning to cultivate resilient, adaptable, and agile learners who are primed for success in a rapidly evolving world.
As you embark on your journey to integrate experiential learning into your educational or professional endeavors, remember that the keys to unlocking its power lie in intentional design, reflective practice, and a commitment to inclusive and impactful learning experiences. By embracing experiential learning as a catalyst for continuous growth and learning, you are poised to revolutionize the way knowledge is acquired, applied, and shared, shaping a future where experiential learning propels individuals and organizations toward unparalleled heights of achievement and innovation.
For Consultation for your experiential learning needs please get in touch with us at [email protected]
FAQ on Experiential Learning
What is Experiential Learning?
Experiential Learning is a widely used teaching and learning method that emphasizes practical, hands-on experience as the primary means of acquiring knowledge and developing skills for the learners. It involves actively engaging with the world around us to gain new knowledge, skills, and perspectives.
How does Experiential Learning work?
Experiential Learning works by placing the learner in real-life challenging situations where they can apply their theoretical knowledge and practice new skills, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding through personal experience.
What are the benefits of Experiential Learning?
Experiential Learning provides learners with a more engaging, relevant, and meaningful learning experience, helping them to retain information better, develop problem-solving skills, and build self-confidence.
What are some examples of Experiential Learning activities?
Some examples of Experiential Learning activities include outdoor group activities, team building, field trips, simulations, role-playing, case studies, and project-based Learning.
How does Experiential Learning differ from traditional teaching methods?
Experiential Learning differs from conventional teaching methods in that it places a greater emphasis on hands-on, real-world experiences, as opposed to lecture-based instruction. This method of learning makes it a more active, engaging, and memorable form of Learning for the participants.
What does experiential learning mean?
Experiential learning theory, developed by David Kolb, suggests that learning is most effective when it involves a cycle of four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
Why is experiential learning important?
Experiential learning is important because it helps learners to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. It also encourages learners to be active participants in their own learning, leading to deeper understanding and greater retention of information.
What is the experiential learning approach?
The experiential learning approach involves designing learning experiences that allow learners to engage actively with the subject matter. This can include simulations, role-playing, project-based learning, and other hands-on activities.
What is experiential learning in education?
In education, experiential learning can be used to enhance traditional classroom instruction and provide students with opportunities to apply what they have learned in real-world settings.
Who created experiential learning?
Experiential learning was first introduced by John Dewey in the early 20th century and later developed by Carl Rogers, David Kolb, and others.
How to implement experiential learning?
To implement experiential learning, educators can incorporate hands-on activities, group work, and reflective exercises into their lesson plans. It is important to provide learners with opportunities to explore and experiment in a safe and supportive environment.
How does experiential learning help adults learn?
Experiential learning benefits adults by providing them with practical skills and knowledge that can be immediately applied in their personal or professional lives. It also promotes lifelong learning and personal growth.
What is Kolb's experiential learning theory?
Kolb's experiential learning theory suggests that learning occurs through a cycle of concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
What are examples of experiential learning?
Examples of experiential learning include internships, study abroad programs, service learning projects, and apprenticeships.
What is the experiential learning cycle?
The experiential learning cycle involves four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
What is Kolb's theory of experiential learning?
Kolb's theory of experiential learning emphasizes the importance of reflection and experimentation in the learning process.
How does experiential learning benefit students?
Experiential learning benefits students learning by providing them with opportunities to apply what they have learned in real-world settings, developing practical skills, and promoting personal growth and self-awareness.
How does Experiential Learning Benefit Training Sessions
Experiential education enhances training sessions by providing hands-on, immersive learning experiences. It fosters deeper understanding, improves retention, and develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By engaging directly with the material, learners can better connect theory with practice, making the learning process more effective and meaningful.
How Experiential Learning can be used in the Classroom?
Experiential learning can be effectively incorporated into the classroom setting through various engaging and interactive activities, such as:
What are Experiential Learning Opportunities?
Experiential learning opportunities can be found in diverse settings, including:
What is Experiential Learning's Impact on Development?
Experiential learning fosters a range of positive developments in learners, including:
What is Pedagogy, Theory, Strategy, or Philosophy in experiential learning?
Experiential learning encompasses various aspects of education:
What is the Importance of Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is crucial for preparing individuals to thrive in the 21st century:
What are some Experiential Learning Quotes?
"Experience is not what happens to you; it is what you do with what happens to you." - Aldous Huxley
"Learning is not attained by chance, it must be sought for with ardour and diligence." - Abigail Adams
"Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn." - Benjamin Franklin
"The best way to learn is by doing." - Aristotle
"We learn by doing, not by listening." - Confucius
What is Authenticity and Implementation in Experiential Learning?
Authentic experiential learning experiences should:
Why Experiential Learning is the Future?
In today's rapidly changing world, traditional methods of education are no longer enough. Employers are looking for workers who are critical thinkers, problem solvers, and adaptable. Experiential learning can help develop these skills and prepare learners for the future of work.
Who Developed Experiential Learning Theory?
Several educators and theorists have contributed to the development of experiential learning theory. Some of the most influential include:
John Dewey: An American philosopher, psychologist, and educational reformer who emphasized the importance of learning through experience.
David Kolb: An American educational theorist who developed a four-stage model of experiential learning.
Kurt Lewin: A German-American psychologist who studied the dynamics of group behavior and developed the concept of action research.
Is Experiential Learning Effective?
Research has shown that experiential learning is an effective approach to education. Learners who participate in experiential learning activities tend to have higher levels of engagement, understanding, and retention than those who learn through traditional methods.
What are Examples of experiential learning activities?
Examples of Experiential Learning Activities:
How is Experiential learning used in education?
Experiential Learning in Education:
How is Experiential learning used in corporate training?
Experiential Learning in Corporate Training:
What is the difference between Experiential learning vs traditional learning?
Experiential vs. Traditional Learning:
Traditional: Passive, teacher-centered, focused on memorization and rote learning.
Experiential: Active, learner-centered, focused on application, reflection, and problem-solving.
How to design experiential learning activities?
Designing Experiential Learning Activities:
How Technology can be used in experiential learning?
Technology in Experiential Learning:
What are Challenges of implementing experiential learning?
Challenges of Implementing Experiential Learning:
What are some Experiential learning resources and tools?
Resources and Tools:
Organizations: AEE, National Clearinghouse for Service-Learning and Civic Engagement.
Websites: iCivics, EVERFI, Quest.
Books: David Kolb's "Experiential Learning," Robert Bjork's "Learning and Memory."
What are Experiential Learning Activities for for Different Age Groups?
What are some Tips for facilitating successful experiential learning activities?
Tips for Successful Experiential Learning Activities:
How to create an experiential learning program for my company?
Creating an Experiential Learning Program for Your Company:
Does experiential learning really work?
Yes, research shows it can be highly effective. Studies demonstrate learners who engage in experiential activities often experience:
Is experiential learning just a fad?
Absolutely not! Its roots go deep in educational history, dating back to early 20th-century educators like John Dewey. Recent years have seen a surge in interest due to its ability to address traditional learning limitations and better prepare students for the 21st-century workforce.
Experiential learning's popularity stems from its emphasis on active learning, critical thinking, and real-world application of knowledge, all crucial skills in today's dynamic world. As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, employers seek individuals with creative problem-solving abilities and collaborative skills. Experiential learning can equip students with these skills and make them stand out in the job market.
Is experiential learning too expensive?
The cost can vary depending on the activity. Some, like field trips or simulations, can be pricier. However, numerous low-cost or even free options exist, such as service learning projects, case studies, and role-playing exercises.
In the long term, experiential learning can actually save money by improving student outcomes. Studies show that students who participate in such programs are more likely to graduate, have higher earning potential, and be more productive employees. These benefits can offset the initial costs of implementing experiential learning programs.
How can I measure the impact of experiential learning?
Several methods exist to measure the impact of experiential learning:
Experiential Learning is a widely used teaching and learning method that emphasizes practical, hands-on experience as the primary means of acquiring knowledge and developing skills for the learners. It involves actively engaging with the world around us to gain new knowledge, skills, and perspectives.
How does Experiential Learning work?
Experiential Learning works by placing the learner in real-life challenging situations where they can apply their theoretical knowledge and practice new skills, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding through personal experience.
What are the benefits of Experiential Learning?
Experiential Learning provides learners with a more engaging, relevant, and meaningful learning experience, helping them to retain information better, develop problem-solving skills, and build self-confidence.
What are some examples of Experiential Learning activities?
Some examples of Experiential Learning activities include outdoor group activities, team building, field trips, simulations, role-playing, case studies, and project-based Learning.
How does Experiential Learning differ from traditional teaching methods?
Experiential Learning differs from conventional teaching methods in that it places a greater emphasis on hands-on, real-world experiences, as opposed to lecture-based instruction. This method of learning makes it a more active, engaging, and memorable form of Learning for the participants.
What does experiential learning mean?
Experiential learning theory, developed by David Kolb, suggests that learning is most effective when it involves a cycle of four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
Why is experiential learning important?
Experiential learning is important because it helps learners to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. It also encourages learners to be active participants in their own learning, leading to deeper understanding and greater retention of information.
What is the experiential learning approach?
The experiential learning approach involves designing learning experiences that allow learners to engage actively with the subject matter. This can include simulations, role-playing, project-based learning, and other hands-on activities.
What is experiential learning in education?
In education, experiential learning can be used to enhance traditional classroom instruction and provide students with opportunities to apply what they have learned in real-world settings.
Who created experiential learning?
Experiential learning was first introduced by John Dewey in the early 20th century and later developed by Carl Rogers, David Kolb, and others.
How to implement experiential learning?
To implement experiential learning, educators can incorporate hands-on activities, group work, and reflective exercises into their lesson plans. It is important to provide learners with opportunities to explore and experiment in a safe and supportive environment.
How does experiential learning help adults learn?
Experiential learning benefits adults by providing them with practical skills and knowledge that can be immediately applied in their personal or professional lives. It also promotes lifelong learning and personal growth.
What is Kolb's experiential learning theory?
Kolb's experiential learning theory suggests that learning occurs through a cycle of concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
What are examples of experiential learning?
Examples of experiential learning include internships, study abroad programs, service learning projects, and apprenticeships.
What is the experiential learning cycle?
The experiential learning cycle involves four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
What is Kolb's theory of experiential learning?
Kolb's theory of experiential learning emphasizes the importance of reflection and experimentation in the learning process.
How does experiential learning benefit students?
Experiential learning benefits students learning by providing them with opportunities to apply what they have learned in real-world settings, developing practical skills, and promoting personal growth and self-awareness.
How does Experiential Learning Benefit Training Sessions
Experiential education enhances training sessions by providing hands-on, immersive learning experiences. It fosters deeper understanding, improves retention, and develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By engaging directly with the material, learners can better connect theory with practice, making the learning process more effective and meaningful.
How Experiential Learning can be used in the Classroom?
Experiential learning can be effectively incorporated into the classroom setting through various engaging and interactive activities, such as:
- Role-playing: Participants assume different roles and act out scenarios or situations to gain insights into different perspectives and challenges.
- Simulations: Learners engage with computer simulations or real-life scenarios to experience and understand complex concepts and processes.
- Case studies: Students analyze real-world business cases to identify problems, develop solutions, and make informed decisions.
- Field trips: Learners visit businesses, organizations, or historical sites to observe real-world applications of concepts and gain exposure to different environments.
- Internships: Students gain practical experience and apply their knowledge in professional settings through internships or apprenticeships.
What are Experiential Learning Opportunities?
Experiential learning opportunities can be found in diverse settings, including:
- Schools: Experiential activities can be integrated into classroom lessons, projects, and extracurricular activities.
- Workplaces: On-the-job training, internships, apprenticeships, and job shadowing programs provide opportunities for experiential learning.
- Communities: Community service projects, volunteer work, and involvement in community organizations offer hands-on experiences and real-world problem-solving opportunities.
What is Experiential Learning's Impact on Development?
Experiential learning fosters a range of positive developments in learners, including:
- Skill Development: Learners gain practical skills in problem-solving, communication, teamwork, and critical thinking through hands-on experiences.
- Knowledge Acquisition: Experiential learning allows for a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge as concepts are applied to real-world situations.
- Motivation Enhancement: Engaging and interactive experiential activities motivate learners and increase their interest in the subject matter.
- Self-Confidence Building: As learners successfully navigate experiential challenges, their self-confidence and belief in their abilities grow.
What is Pedagogy, Theory, Strategy, or Philosophy in experiential learning?
Experiential learning encompasses various aspects of education:
- Pedagogy: It represents a specific teaching approach that emphasizes active learning experiences.
- Theory: It is grounded in psychological theories that explain how individuals learn through experience.
- Teaching Strategy: It provides a practical framework for designing and implementing engaging learning activities.
- Philosophy: It reflects a belief that learning is most effective when it is connected to real-world experiences and personal reflection.
What is the Importance of Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is crucial for preparing individuals to thrive in the 21st century:
- Relevance: It connects learning to real-world applications, making knowledge more relevant and meaningful.
- Engagement: It promotes active participation, fostering a more engaging and motivating learning environment.
- Skill Development: It cultivates practical skills that are essential for success in the workplace and beyond.
- Critical Thinking: It encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
- Lifelong Learning: It fosters a lifelong learning mindset, encouraging individuals to continue learning and adapting throughout their lives.
What are some Experiential Learning Quotes?
"Experience is not what happens to you; it is what you do with what happens to you." - Aldous Huxley
"Learning is not attained by chance, it must be sought for with ardour and diligence." - Abigail Adams
"Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn." - Benjamin Franklin
"The best way to learn is by doing." - Aristotle
"We learn by doing, not by listening." - Confucius
What is Authenticity and Implementation in Experiential Learning?
Authentic experiential learning experiences should:
- Be relevant to the learner's interests and goals
- Provide opportunities for deep engagement and reflection
- Allow for self-discovery and skill development
- Be connected to real-world applications
Why Experiential Learning is the Future?
In today's rapidly changing world, traditional methods of education are no longer enough. Employers are looking for workers who are critical thinkers, problem solvers, and adaptable. Experiential learning can help develop these skills and prepare learners for the future of work.
Who Developed Experiential Learning Theory?
Several educators and theorists have contributed to the development of experiential learning theory. Some of the most influential include:
John Dewey: An American philosopher, psychologist, and educational reformer who emphasized the importance of learning through experience.
David Kolb: An American educational theorist who developed a four-stage model of experiential learning.
Kurt Lewin: A German-American psychologist who studied the dynamics of group behavior and developed the concept of action research.
Is Experiential Learning Effective?
Research has shown that experiential learning is an effective approach to education. Learners who participate in experiential learning activities tend to have higher levels of engagement, understanding, and retention than those who learn through traditional methods.
What are Examples of experiential learning activities?
Examples of Experiential Learning Activities:
- Simulations: Run a virtual business, navigate historical events through role-playing, dissect virtual frogs in science class.
- Case Studies: Analyze real-world scenarios and propose solutions in various fields like marketing or healthcare.
- Fieldwork/Service Learning: Conduct research in nature, volunteer at a non-profit, or intern at a company.
- Creative Projects: Design a prototype, write a song, create presentations to apply knowledge in engaging ways.
- Debates/Discussions: Engage in critical thinking and communication by arguing different perspectives on a topic.
How is Experiential learning used in education?
Experiential Learning in Education:
- Promotes active learning and deeper understanding.
- Personalizes learning and connects knowledge to personal lives.
- Develops essential skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration.
- Makes learning relevant to future careers by showcasing real-world applications.
How is Experiential learning used in corporate training?
Experiential Learning in Corporate Training:
- Boosts employee engagement and retention through interactive learning.
- Develops essential skills like leadership, communication, teamwork, and decision-making.
- Encourages innovation and creativity by thinking outside the box.
- Leads to better knowledge retention through active participation and reflection.
What is the difference between Experiential learning vs traditional learning?
Experiential vs. Traditional Learning:
Traditional: Passive, teacher-centered, focused on memorization and rote learning.
Experiential: Active, learner-centered, focused on application, reflection, and problem-solving.
How to design experiential learning activities?
Designing Experiential Learning Activities:
- Define learning objectives: What knowledge, skills, and attitudes do you want participants to gain?
- Choose appropriate activities: Align activities with objectives, consider age, resources, learning styles.
- Scaffold and support: Guide learners through the process and offer feedback.
- Facilitate reflection: Encourage critical thinking about experiences and connection to concepts.
How Technology can be used in experiential learning?
Technology in Experiential Learning:
- VR simulations: Immerse learners in realistic scenarios for deeper understanding.
- Gamification: Make learning interactive and engaging with game mechanics and rewards.
- Collaboration tools: Facilitate teamwork and communication through online platforms.
- Data analysis: Track progress and measure the impact of activities.
What are Challenges of implementing experiential learning?
Challenges of Implementing Experiential Learning:
- Time and resources: Designing and implementing activities can be time-consuming and require additional resources.
- Assessment: Measuring the impact can be complex and require new assessment methods.
- Faculty/trainer development: Educators/trainers need training to effectively design and facilitate activities.
What are some Experiential learning resources and tools?
Resources and Tools:
Organizations: AEE, National Clearinghouse for Service-Learning and Civic Engagement.
Websites: iCivics, EVERFI, Quest.
Books: David Kolb's "Experiential Learning," Robert Bjork's "Learning and Memory."
What are Experiential Learning Activities for for Different Age Groups?
- Early childhood: Play-based learning, exploration, discovery through senses and interactions.
- K-12: Project-based learning, simulations, field trips, service learning.
- Higher education: Internships, research projects, study abroad, case studies.
- Adult learners: Job-embedded learning, workshops, simulations, mentoring programs.
What are some Tips for facilitating successful experiential learning activities?
Tips for Successful Experiential Learning Activities:
- Clear objectives and expectations.
- Active participation and engagement.
- Safe and supportive learning environment.
- Reflection and discussion.
- Feedback and continuous improvement.
How to create an experiential learning program for my company?
Creating an Experiential Learning Program for Your Company:
- Identify learning goals and target audience.
- Choose formats and activities based on goals and audience.
- Develop clear instructions and expectations.
- Provide feedback and support to participants.
- Evaluate program effectiveness and make adjustments.
Does experiential learning really work?
Yes, research shows it can be highly effective. Studies demonstrate learners who engage in experiential activities often experience:
- Deeper understanding and knowledge retention.
- Sharpened critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Boosted creativity and innovative thinking.
- Enhanced communication and collaboration skills.
- Elevated motivation and engagement in learning.
Is experiential learning just a fad?
Absolutely not! Its roots go deep in educational history, dating back to early 20th-century educators like John Dewey. Recent years have seen a surge in interest due to its ability to address traditional learning limitations and better prepare students for the 21st-century workforce.
Experiential learning's popularity stems from its emphasis on active learning, critical thinking, and real-world application of knowledge, all crucial skills in today's dynamic world. As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, employers seek individuals with creative problem-solving abilities and collaborative skills. Experiential learning can equip students with these skills and make them stand out in the job market.
Is experiential learning too expensive?
The cost can vary depending on the activity. Some, like field trips or simulations, can be pricier. However, numerous low-cost or even free options exist, such as service learning projects, case studies, and role-playing exercises.
In the long term, experiential learning can actually save money by improving student outcomes. Studies show that students who participate in such programs are more likely to graduate, have higher earning potential, and be more productive employees. These benefits can offset the initial costs of implementing experiential learning programs.
How can I measure the impact of experiential learning?
Several methods exist to measure the impact of experiential learning:
- Pre- and post-assessments: These measure changes in knowledge, skills, and attitudes before and after an activity.
- Observation: Observing learners during an activity can reveal their engagement, participation, and problem-solving skills.
- Feedback: Asking learners for feedback on their experience provides valuable insights into their learning and gains from the activity.
- Performance measures: Tracking learner performance on tasks related to the learning objectives reveals the activity's impact.
- Portfolio assessment: Having learners collect and reflect on their work throughout the learning process offers a holistic view of their learning and progress.
How to reference this article:
Diyanat Ali (2018, July 24), Experiential Learning Models, Methods, Principles, & Practices
Outlife - https://www.outlife.in/experiential-learning.html
Diyanat Ali (2018, July 24), Experiential Learning Models, Methods, Principles, & Practices
Outlife - https://www.outlife.in/experiential-learning.html